SARS spike protein induces phenotypic conversion of human B cells to macrophage-like cells
- PMID: 20667598
- PMCID: PMC7112600
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.06.014
SARS spike protein induces phenotypic conversion of human B cells to macrophage-like cells
Abstract
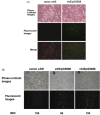
Massive aggregations of macrophages are frequently detected in afflicted lungs of patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection. In vitro, ectopic expression of transcription factors, in particular CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPα) and C/EBPβ, can convert B cells into functional macrophages. However, little is known about the specific ligands responsible for such phenotype conversion. Here, we investigated whether spike protein of SARS-CoV can act as a ligand to trigger the conversion of B cells to macrophages. We transduced SARS-CoV spike protein-displayed recombinant baculovirus (SSDRB), vAtEpGS688, into peripheral B cells and B lymphoma cells. Cell surface expression of CD19 or Mac-1 (CD11b) was determined by flow cytometry. SSDRB-mediated changes in gene expression profiles of B lymphoma cells were analyzed by microarray. In this report, we showed that spike protein of SARS virus could induce phenotypic conversion of human B cells, either from peripheral blood or B lymphoma cells, to macrophage-like cells that were steadily losing the B-cell marker CD19 and in turn expressing the macrophage-specific marker Mac-1. Furthermore, we found that SSDRB enhanced the expression of CD86, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF1α), suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS or STAT-induced STAT inhibitor)-3, C/EBPβ, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), Krüpple-like factor (KLF)-5, and CD54, without marked influence on C/EBPα or PU.1 expression in transduced cells. Prolonged exposure to hypoxia could also induce macrophage-like conversion of B cells. These macrophage-like cells were defective in phagocytosis of red fluorescent beads. In conclusion, our results suggest that conversion of B cells to macrophage-like cells, similar to a pathophysiological response, could be mediated by a devastating viral ligand, in particular spike protein of SARS virus, or in combination with severe local hypoxia, which is a condition often observed in afflicted lungs of SARS patients.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Upregulation of the chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 via a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike-ACE2 signaling pathway.J Virol. 2010 Aug;84(15):7703-12. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02560-09. Epub 2010 May 19. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20484496 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of murine CD8 T cell epitopes in codon-optimized SARS-associated coronavirus spike protein.Virology. 2005 Apr 25;335(1):34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.01.050. Virology. 2005. PMID: 15823604 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of IL-6 and TNF-alpha induced by SARS-coronavirus spike protein in murine macrophages via NF-kappaB pathway.Virus Res. 2007 Sep;128(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.02.007. Epub 2007 May 25. Virus Res. 2007. PMID: 17532082 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of the spike glycoprotein of bat SARS-like coronavirus.Virol Sin. 2010 Feb;25(1):36-44. doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3096-2. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Virol Sin. 2010. PMID: 20960282 Free PMC article.
-
SARS patients-derived human recombinant antibodies to S and M proteins efficiently neutralize SARS-coronavirus infectivity.Biomed Environ Sci. 2005 Dec;18(6):363-74. Biomed Environ Sci. 2005. PMID: 16544518
Cited by
-
COVID-19 disease and autoimmune disorders: A mutual pathway.World J Methodol. 2022 Jul 20;12(4):200-223. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i4.200. eCollection 2022 Jul 20. World J Methodol. 2022. PMID: 36159097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and the type I interferon response.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Jul 29;16(7):e1008737. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008737. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32726355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The secret life of viral entry glycoproteins: moonlighting in immune evasion.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(5):e1003258. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003258. Epub 2013 May 16. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23696729 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Pro-inflammatory microenvironment and systemic accumulation of CXCR3+ cell exacerbate lung pathology of old rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Sep 1;6(1):328. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00734-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34471088 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of the activation of unfolded protein response by spike proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and human coronavirus HKU1.Cell Biosci. 2014 Jan 13;4(1):3. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-4-3. Cell Biosci. 2014. PMID: 24410900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akashi K., Traver D., Miyamoto T., Weissman I.L. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature. 2000;404:193–197. - PubMed
-
- Alcivar A., Hu S., Tang J., Yang X. DEDD and DEDD2 associate with caspase-8/10 and signal cell death. Oncogene. 2003;22:291–297. - PubMed
-
- Alexander W.S. Cytokines in hematopoiesis. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1998;16:651–682. - PubMed
-
- Anand R.J., Gribar S.C., Li J., Kohler J.W., Branca M.F., Dubowski T., Sodhi C.P., Hackam D.J. Hypoxia causes an increase in phagocytosis by macrophages in a HIF-1α-dependent manner. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007;82:1257–1265. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y.J., Liu C.Y., Chiang B.L., Chao Y.C., Chen C.C. Induction of IL-8 release in lung cells via activator protein-1 by recombinant baculovirus displaying severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus spike proteins: identification of two functional regions. J. Immunol. 2004;173:7602–7614. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

