Behavioral deficits and progressive neuropathology in progranulin-deficient mice: a mouse model of frontotemporal dementia
- PMID: 20667979
- PMCID: PMC2992364
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.10-161471
Behavioral deficits and progressive neuropathology in progranulin-deficient mice: a mouse model of frontotemporal dementia
Abstract
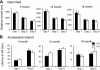
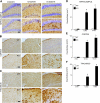
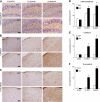
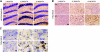
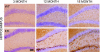
Progranulin haploinsufficiency causes frontotemporal dementia with tau-negative, ubiquitin-positive neuronal inclusion pathology. In this study, we showed that progranulin-deficient mice displayed increased depression- and disinhibition-like behavior, as well as deficits in social recognition from a relatively young age. These mice did not have any deficit in locomotion or exploration. Eighteen-month-old progranulin-deficient mice demonstrated impaired spatial learning and memory in the Morris water maze. In addition to behavioral deficits, progranulin-deficient mice showed a progressive development of neuropathology from 12 mo of age, including enhanced activation of microglia and astrocytes and ubiquitination and cytoplasmic accumulation of phosphorylated TDP-43. Thus, progranulin deficiency induced FTD-like behavioral and neuropathological deficits. These mice may serve as an important tool for deciphering underlying mechanisms in frontotemporal dementia.
Figures
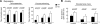
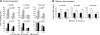
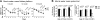
References
-
- Baba T., Hoff H. B., 3rd, Nemoto H., Lee H., Orth J., Arai Y., Gerton G. L. (1993) Acrogranin, an acrosomal cysteine-rich glycoprotein, is the precursor of the growth-modulating peptides, granulins, and epithelins, and is expressed in somatic as well as male germ cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 34, 233–243 - PubMed
-
- He Z., Bateman A. (2003) Progranulin (granulin-epithelin precursor, PC-cell-derived growth factor, acrogranin) mediates tissue repair and tumorigenesis. J. Mol. Med. 81, 600–612 - PubMed
-
- Daniel R., Daniels E., He Z., Bateman A. (2003) Progranulin (acrogranin/PC cell-derived growth factor/granulin-epithelin precursor) is expressed in the placenta, epidermis, microvasculature, and brain during murine development. Dev. Dyn. 227, 593–599 - PubMed
-
- Zhu J., Nathan C., Jin W., Sim D., Ashcroft G. S., Wahl S. M., Lacomis L., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Wright C. D., Ding A. (2002) Conversion of proepithelin to epithelins: roles of SLPI and elastase in host defense and wound repair. Cell 111, 867–878 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

