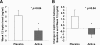Effects of recombinant human growth hormone in anorexia nervosa: a randomized, placebo-controlled study
- PMID: 20668047
- PMCID: PMC2968733
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2010-0493
Effects of recombinant human growth hormone in anorexia nervosa: a randomized, placebo-controlled study
Abstract
Context: Anorexia nervosa (AN), a state of chronic nutritional deprivation, is characterized by GH resistance with elevated GH levels and decreased levels of IGF-I. The effects of supraphysiological recombinant human GH (rhGH) on GH resistance in AN are not currently known.
Objective: The aim was to investigate whether supraphysiological rhGH increases IGF-I levels in AN.
Design and setting: We conducted a randomized, placebo-controlled study in a Clinical Research Center.
Patients: We studied 21 women with AN, 10 (mean age, 28 ± 2.1 yr) treated with rhGH and 11 (mean age, 29.2 ± 2.6 yr) treated with placebo.
Interventions: rhGH (mean maximum daily dose, 1.4 ± 0.12 mg/d) or placebo was administered to patients for 12 wk.
Main outcome measures: IGF-I, N-terminal propeptide of type 1 procollagen, type I collagen C-telopeptide, glucose, and insulin levels were measured at wk 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, and 12; C-terminal propeptide of type 1 procollagen, leptin, and free fatty acid levels were measured at wk 0 and 12. Body composition, including total fat and lean mass, was measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry at wk 0 and 12.
Results: IGF-I levels did not differ between the groups at baseline or after treatment (median after 12 wk-rhGH, 124 ng/ml, interquartile range, 94.5, 170.3; vs. placebo, 85.5 ng/ml, interquartile range, 62, 139; P = 0.3). Similarly, changes in glucose, insulin, free fatty acids, and bone markers did not differ between the groups. Total fat mass and percentage fat mass (rhGH, -2.5 ± 0.6%, vs. placebo, 2.2 ± 1.1%; P = 0.004) decreased significantly in the rhGH group compared to placebo despite comparable weight.
Conclusions: Supraphysiological rhGH administration decreases fat mass in AN without increasing IGF-I levels, supporting the role of GH as a mediator of lipolysis independent of IGF-I.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Administration of recombinant human growth hormone normalizes GH-IGF1 axis and improves malnutrition-related disorders in patients with anorexia nervosa.Endocr J. 2007 Apr;54(2):319-27. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.k05-178. Epub 2007 Mar 6. Endocr J. 2007. Retraction in: Endocr J. 2009;56(5):726. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.not09-01. PMID: 17339748 Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Metabolic effects of biosynthetic growth hormone treatment in severely energy-restricted obese women.Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998 Sep;22(9):836-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0800669. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998. PMID: 9756240 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) supplementation on adipokines and C-reactive protein in obese subjects.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2007 Feb;17(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2006.10.001. Epub 2006 Nov 22. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2007. PMID: 17118687 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of short-term recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I administration on bone turnover in osteopenic women with anorexia nervosa.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Nov;81(11):3864-70. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.11.8923830. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996. PMID: 8923830 Clinical Trial.
-
Fibroblast growth factor-21 may mediate growth hormone resistance in anorexia nervosa.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Jan;95(1):369-74. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-1730. Epub 2009 Nov 19. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 19926712 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea: Impact on bone and neuropsychiatric outcomes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 22;13:953180. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.953180. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35937789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Teriparatide increases bone formation and bone mineral density in adult women with anorexia nervosa.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Apr;99(4):1322-9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-4105. Epub 2014 Jan 23. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24456286 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Determinants of GH resistance in malnutrition.J Endocrinol. 2014 Jan 27;220(3):R57-65. doi: 10.1530/JOE-13-0477. Print 2014 Mar. J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24363451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anorexia nervosa, obesity and bone metabolism.Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2013 Sep;11(1):21-33. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24079076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Route of Estrogen Administration on Bone Turnover Markers in Oligoamenorrheic Athletes and Its Mediators.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019 May 1;104(5):1449-1458. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-02143. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30476179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pope Jr HG, Hudson JI, Yurgelun-Todd D, Hudson MS 1984 Prevalence of anorexia nervosa and bulimia in three student populations. Int J Eat Disord 3:45–51
-
- Lucas AR, Beard CM, O'Fallon WM, Kurland LT 1991 50-year trends in the incidence of anorexia nervosa in Rochester, Minn.: a population-based study. Am J Psychiatry 148:917–922 - PubMed
-
- Mayer L, Walsh BT, Pierson Jr RN, Heymsfield SB, Gallagher D, Wang J, Parides MK, Leibel RL, Warren MP, Killory E, Glasofer D 2005 Body fat redistribution after weight gain in women with anorexia nervosa. Am J Clin Nutr 81:1286–1291 - PubMed
-
- Scacchi M, Pincelli AI, Caumo A, Tomasi P, Delitala G, Baldi G, Cavagnini F 1997 Spontaneous nocturnal growth hormone secretion in anorexia nervosa. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:3225–3229 - PubMed
-
- Støving RK, Veldhuis JD, Flyvbjerg A, Vinten J, Hangaard J, Koldkjaer OG, Kristiansen J, Hagen C 1999 Jointly amplified basal and pulsatile growth hormone (GH) secretion and increased process irregularity in women with anorexia nervosa: indirect evidence for disruption of feedback regulation within the GH-insulin-like growth factor I axis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:2056–2063 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources