Oncogenic Wip1 phosphatase is inhibited by miR-16 in the DNA damage signaling pathway
- PMID: 20668064
- PMCID: PMC2940956
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0697
Oncogenic Wip1 phosphatase is inhibited by miR-16 in the DNA damage signaling pathway
Abstract
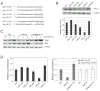
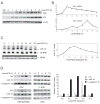
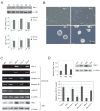
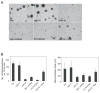
Wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (Wip1) was identified as an oncogene amplified and overexpressed in several human cancers. Recent evidence suggested that Wip1 is a critical inhibitor in the ATM/ATR-p53 DNA damage signaling pathway. Wip1 dephosphorylates several key DNA damage-responsive proteins and reverses DNA damage-induced cell cycle checkpoints. Previous reports showed that Wip1 was transcriptionally induced by p53 at the early stage of the DNA damage response. To investigate the temporal and functional regulation of Wip1, we identified a microRNA, miR-16, that specifically targets the mRNA of Wip1 and thus negatively regulates the expression level of Wip1. miR-16 itself is induced immediately after DNA damage. Therefore, the increase in Wip1 protein level is significantly postponed compared with that of its mRNA level, preventing a premature inactivation of ATM/ATR signaling and allowing a functional completion of the early DNA damage response. To better understand miR-16 biological functions in the context of cancer cells, we examined its expression in mammary tumor stem cells and found it to be markedly downregulated in mammary tumor stem cells. Overexpression of miR-16 or inhibition of Wip1 suppresses the self-renewal and growth of mouse mammary tumor stem cells and sensitizes MCF-7 human breast cancer cells to the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Together, our results suggest an important role of miR-16 in the regulation of Wip1 phosphatase in the DNA damage response and mammary tumorigenesis.
©2010 AACR.
Figures

Similar articles
-
P65-mediated miR-590 inhibition modulates the chemoresistance of osteosarcoma to doxorubicin through targeting wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):5652-5665. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27849. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30387173
-
The estrogen receptor alpha pathway induces oncogenic Wip1 phosphatase gene expression.Mol Cancer Res. 2009 May;7(5):713-23. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0247. Epub 2009 May 12. Mol Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19435816
-
Down-regulation of wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (Wip1) plays a critical role in regulating several p53-dependent functions in premature senescent tumor cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 7;288(23):16212-16224. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.435149. Epub 2013 Apr 23. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23612976 Free PMC article.
-
The type 2C phosphatase Wip1: an oncogenic regulator of tumor suppressor and DNA damage response pathways.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008 Jun;27(2):123-35. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9127-x. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008. PMID: 18265945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the Wip1 phosphatase and its effects on the stress response.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jan 1;17(4):1480-98. doi: 10.2741/3999. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22201816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How Diet Intervention via Modulation of DNA Damage Response through MicroRNAs May Have an Effect on Cancer Prevention and Aging, an in Silico Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 19;17(5):752. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050752. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27213347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Activation, p53, and Autophagy Inhibition Characterize the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Spike Protein Induced Neurotoxicity.Cureus. 2022 Dec 9;14(12):e32361. doi: 10.7759/cureus.32361. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36514706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wip1 phosphatase in breast cancer.Oncogene. 2015 Aug 20;34(34):4429-38. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.375. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25381821 Review.
-
microRNA expression and biogenesis in cellular response to ionizing radiation.DNA Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;33(10):667-79. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2401. Epub 2014 Jun 6. DNA Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24905898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA damage response revisited: the p53 family and its regulators provide endless cancer therapy opportunities.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Oct;54(10):1658-1669. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00863-4. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36207426 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lu X, Nguyen TA, Donehower LA. Reversal of the ATM/ATR-mediated DNA damage response by the oncogenic phosphatase PPM1D. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:1060–4. - PubMed
-
- Shreeram S, Demidov ON, Hee WK, et al. Wip1 phosphatase modulates ATM-dependent signaling pathways. Mol Cell. 2006;23:757–64. - PubMed
-
- Fujimoto H, Onishi N, Kato N, et al. Regulation of the antioncogenic Chk2 kinase by the oncogenic Wip1 phosphatase. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:1170–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

