Genetic variants of human organic anion transporter 4 demonstrate altered transport of endogenous substrates
- PMID: 20668102
- PMCID: PMC2957254
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00312.2010
Genetic variants of human organic anion transporter 4 demonstrate altered transport of endogenous substrates
Abstract
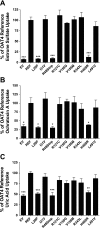
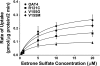
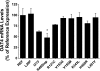
Apical reabsorption from the urine has been shown to be important for such processes as the maintenance of critical metabolites in the blood and the excretion of nephrotoxic compounds. The solute carrier (SLC) transporter OAT4 (SLC22A11) is expressed on the apical membrane of renal proximal tubule cells and is known to mediate the transport of a variety of xenobiotic and endogenous organic anions. Functional characterization of genetic variants of apical transporters thought to mediate reabsorption, such as OAT4, may provide insight into the genetic factors influencing the complex pathways involved in drug elimination and metabolite reclamation occurring in the kidney. Naturally occurring genetic variants of OAT4 were identified in public databases and by resequencing DNA samples from 272 individuals comprising 4 distinct ethnic groups. Nine total nonsynonymous variants were identified and functionally assessed using uptake of three radiolabeled substrates. A nonsense variant, R48Stop, and three other variants (R121C, V155G, and V155M) were found at frequencies of at least 2% in an ethnic group specific fashion. The L29P, R48Stop, and H469R variants displayed a complete loss of function, and kinetic analysis identified a reduced V(max) in the common nonsynonymous variants. Plasma membrane levels of OAT4 protein were absent or reduced in the nonfunctional variants, providing a mechanistic reason for the observed loss of function. Characterization of the genetic variants of reabsorptive transporters such as OAT4 is an important step in understanding variability in tubular reabsorption with important implications in innate homeostatic processes and drug disposition.
Figures
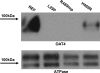
Similar articles
-
Analyses of coding region polymorphisms in apical and basolateral human organic anion transporter (OAT) genes [OAT1 (NKT), OAT2, OAT3, OAT4, URAT (RST)].Kidney Int. 2005 Oct;68(4):1491-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00612.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 16164626
-
Human organic anion transporter 4 is a renal apical organic anion/dicarboxylate exchanger in the proximal tubules.J Pharmacol Sci. 2004 Mar;94(3):297-304. doi: 10.1254/jphs.94.297. J Pharmacol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15037815
-
The human organic anion transporter 3 (OAT3; SLC22A8): genetic variation and functional genomics.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Apr;290(4):F905-12. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00272.2005. Epub 2005 Nov 15. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16291576
-
Urate Transporters in the Kidney: What Clinicians Need to Know.Electrolyte Blood Press. 2021 Jun;19(1):1-9. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2021.19.1.1. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2021. PMID: 34290818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal organic anion transporters in drug-drug interactions and diseases.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018 Jan 15;112:8-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 29109021 Review.
Cited by
-
Attenuated Ochratoxin A Transporter Expression in a Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Protects against Proximal Convoluted Tubule Toxicity.Drug Metab Dispos. 2022 Oct;50(10):1389-1395. doi: 10.1124/dmd.121.000451. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Drug Metab Dispos. 2022. PMID: 34921099 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the Association of Rare Allelic Variants in Urate Transporters SLC22A11, SLC22A13, and SLC17A1 with Hyperuricemia and Gout.Dis Markers. 2024 Jan 6;2024:5930566. doi: 10.1155/2024/5930566. eCollection 2024. Dis Markers. 2024. PMID: 38222853 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic models describing active renal reabsorption and secretion: a simulation-based study.AAPS J. 2013 Jan;15(1):278-87. doi: 10.1208/s12248-012-9437-3. Epub 2012 Nov 30. AAPS J. 2013. PMID: 23196805 Free PMC article.
-
A common 5'-UTR variant in MATE2-K is associated with poor response to metformin.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Nov;90(5):674-84. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2011.165. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21956618 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of 14 PFAS for permeability and organic anion transporter interactions: Implications for renal clearance in humans.Chemosphere. 2024 Aug;361:142390. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.142390. Epub 2024 May 25. Chemosphere. 2024. PMID: 38801906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakhiya N, Monien B, Frank H, Seidel A, Glatt H. Renal organic anion transporters OAT1 and OAT3 mediate the cellular accumulation of 5-sulfooxymethylfurfural, a reactive, nephrotoxic metabolite of the Maillard product 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Biochem Pharmacol 78: 414–419, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Capriotti E, Calabrese R, Casadio R. Predicting the insurgence of human genetic diseases associated to single point protein mutations with support vector machines and evolutionary information. Bioinformatics 22: 2729–2734, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Cha SH, Sekine T, Kusuhara H, Yu E, Kim JY, Kim DK, Sugiyama Y, Kanai Y, Endou H. Molecular cloning and characterization of multispecific organic anion transporter 4 expressed in the placenta. J Biol Chem 275: 4507–4512, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

