T-cell regulation by casitas B-lineage lymphoma (Cblb) is a critical failsafe against autoimmune disease due to autoimmune regulator (Aire) deficiency
- PMID: 20668237
- PMCID: PMC2930471
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1009209107
T-cell regulation by casitas B-lineage lymphoma (Cblb) is a critical failsafe against autoimmune disease due to autoimmune regulator (Aire) deficiency
Abstract
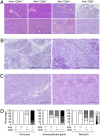
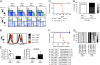
Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome type 1 (APS1) results from homozygous Aire mutations that cripple thymic deletion of organ-specific T cells. The clinical course in man and mouse is characterized by high variability both in the latent period before onset of autoimmune disease and in the specific organs affected, but the reasons for this are unknown. Here we test the hypothesis that the latent period reflects the failsafe action of discrete postthymic mechanisms for imposing self-tolerance in peripheral T cells. Aire-deficient mice were crossed with mice of a uniform major histocompatibility complex (MHC) haplotype and genetic background carrying specific genetic defects in one of four distinct peripheral tolerance mechanisms: activation-induced cell death (Fasl(gld/gld)), anergy and requirement for CD28 costimulation (Cblb(-/-)), inhibition of ICOS and T(FH) cells (Rc3h1(san/san)), or decreased numbers of Foxp3(+) T regulatory cells (Card11(unm/unm)). Cblb-deficiency was unique among these four in precipitating rapid clinical autoimmune disease when combined with Aire-deficiency, resulting in autoimmune exocrine pancreatitis with median age of survival of only 25 d. Massive lymphocytic infiltration selectively destroyed most of the exocrine acinar cells of the pancreas and submandibular salivary gland, and CD4(+) and CD8(+) subsets were necessary and sufficient to transfer the disease. Intrinsic regulation of peripheral T cells by CBL-B thus serves a uniquely critical role as a failsafe against clinical onset of autoimmune disease in AIRE deficiency, and multiple peripheral tolerance mechanisms may need to fail before onset of clinical autoimmunity to many organs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Visualizing the role of Cbl-b in control of islet-reactive CD4 T cells and susceptibility to type 1 diabetes.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 15;186(4):2024-32. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002296. Epub 2011 Jan 19. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21248249
-
Reinforcement of cancer immunotherapy by adoptive transfer of cblb-deficient CD8+ T cells combined with a DC vaccine.Immunol Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;90(1):130-4. doi: 10.1038/icb.2011.11. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 21383769
-
Autoimmune regulator (AIRE)-deficient CD8+CD28low regulatory T lymphocytes fail to control experimental colitis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 26;108(30):12437-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107136108. Epub 2011 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21746930 Free PMC article.
-
Central tolerance to self revealed by the autoimmune regulator.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 Nov;1356(1):80-9. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12960. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 26579596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Twenty Years of AIRE.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 12;9:98. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00098. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29483906 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lymphopenia-induced proliferation in aire-deficient mice helps to explain their autoimmunity and differences from human patients.Front Immunol. 2014 Feb 13;5:51. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00051. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24592265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of immune cell infiltration characteristics in severe acute pancreatitis through integrated bioinformatics.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 15;14(1):8711. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59205-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38622245 Free PMC article.
-
Late-onset autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1: a case report and literature review.Immunol Res. 2021 Apr;69(2):139-144. doi: 10.1007/s12026-021-09180-w. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33599910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoflurane decreases interleukin-2 production by increasing c-Cbl and Cbl-b expression in rat peripheral blood mononuclear cells.J Int Med Res. 2018 Jul;46(7):2792-2802. doi: 10.1177/0300060518770955. Epub 2018 Jun 24. J Int Med Res. 2018. PMID: 29938552 Free PMC article.
-
Does antigen masking by ubiquitin chains protect from the development of autoimmune diseases?Front Immunol. 2014 Jun 3;5:262. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00262. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24917867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hyttinen V, Kaprio J, Kinnunen L, Koskenvuo M, Tuomilehto J. Genetic liability of type 1 diabetes and the onset age among 22,650 young Finnish twin pairs: A nationwide follow-up study. Diabetes. 2003;52:1052–1055. - PubMed
-
- Todd JA, Wicker LS. Genetic protection from the inflammatory disease type 1 diabetes in humans and animal models. Immunity. 2001;15:387–395. - PubMed
-
- Wandstrat A, Wakeland E. The genetics of complex autoimmune diseases: Non-MHC susceptibility genes. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:802–809. - PubMed
-
- Goodnow CC. Multistep pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Cell. 2007;130:25–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

