Bilirubin glucuronidation revisited: proper assay conditions to estimate enzyme kinetics with recombinant UGT1A1
- PMID: 20668247
- PMCID: PMC2967393
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.110.033829
Bilirubin glucuronidation revisited: proper assay conditions to estimate enzyme kinetics with recombinant UGT1A1
Abstract
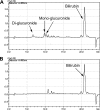
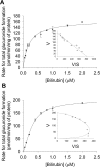
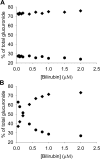
Bilirubin, an end product of heme catabolism, is primarily eliminated via glucuronic acid conjugation by UGT1A1. Impaired bilirubin conjugation, caused by inhibition of UGT1A1, can result in clinical consequences, including jaundice and kernicterus. Thus, evaluation of the ability of new drug candidates to inhibit UGT1A1-catalyzed bilirubin glucuronidation in vitro has become common practice. However, the instability of bilirubin and its glucuronides presents substantial technical challenges to conduct in vitro bilirubin glucuronidation assays. Furthermore, because bilirubin can be diglucuronidated through a sequential reaction, establishment of initial rate conditions can be problematic. To address these issues, a robust high-performance liquid chromatography assay to measure both bilirubin mono- and diglucuronide conjugates was developed, and the incubation conditions for bilirubin glucuronidation by human embryonic kidney 293-expressed UGT1A1 were carefully characterized. Our results indicated that bilirubin glucuronidation should be assessed at very low protein concentrations (0.05 mg/ml protein) and over a short incubation time (5 min) to assure initial rate conditions. Under these conditions, bilirubin total glucuronide formation exhibited a hyperbolic (Michaelis-Menten) kinetic profile with a K(m) of ∼0.2 μM. In addition, under these initial rate conditions, the relative proportions between the total monoglucuronide and the diglucuronide product were constant across the range of bilirubin concentration evaluated (0.05-2 μM), with the monoglucuronide being the predominant species (∼70%). In conclusion, establishment of appropriate incubation conditions (i.e., very low protein concentrations and short incubation times) is necessary to properly characterize the kinetics of bilirubin glucuronidation in a recombinant UGT1A1 system.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous determination of bilirubin and its glucuronides in liver microsomes and recombinant UGT1A1 enzyme incubation systems by HPLC method and its application to bilirubin glucuronidation studies.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Apr;92:149-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.01.025. Epub 2014 Jan 27. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 24525562
-
A Novel Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Estimation of Bilirubin Glucuronides and its Application to In Vitro Enzyme Assays.Drug Metab Lett. 2017;10(4):264-269. doi: 10.2174/1872312810666161124143522. Drug Metab Lett. 2017. PMID: 27908259
-
Estimating the Differences of UGT1A1 Activity in Recombinant UGT1A1 Enzyme, Human Liver Microsomes and Rat Liver Microsome Incubation Systems in Vitro.Biol Pharm Bull. 2015;38(12):1910-7. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b15-00513. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015. PMID: 26632182
-
Unusual glucuronides.Drug Metab Dispos. 2012 Jul;40(7):1239-51. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.045096. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012. PMID: 22517971 Review.
-
The HELP-UnaG Fusion Protein as a Bilirubin Biosensor: From Theory to Mature Technological Development.Molecules. 2025 Jan 21;30(3):439. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030439. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942546 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An ultra-sensitive and easy-to-use assay for sensing human UGT1A1 activities in biological systems.J Pharm Anal. 2020 Jun;10(3):263-270. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2020.05.005. Epub 2020 May 23. J Pharm Anal. 2020. PMID: 32612873 Free PMC article.
-
A UGT1A1 variant is associated with serum total bilirubin levels, which are causal for hypertension in African-ancestry individuals.NPJ Genom Med. 2021 Jun 11;6(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s41525-021-00208-6. NPJ Genom Med. 2021. PMID: 34117260 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic expression of transcription factors affecting developmental regulation of UGT1A1 in the Han Chinese population.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jan;73(1):29-37. doi: 10.1007/s00228-016-2137-7. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27704169
-
Conjugated bilirubin affects cytokine profiles in hepatitis A virus infection by modulating function of signal transducer and activator of transcription factors.Immunology. 2014 Dec;143(4):578-87. doi: 10.1111/imm.12336. Immunology. 2014. PMID: 24943111 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Model of hUGT1A1-modRNA Encoding for the UGT1A1 Enzyme to Treat Crigler-Najjar Syndrome Type 1.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;7(6):404-412. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12301. Epub 2018 Apr 26. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29637732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi S, Uesugi T, Kamisaka K. (1985) Study of bilirubin metabolism by high-performance liquid chromatography: stability of bilirubin glucuronides. Arch Biochem Biophys 241:486–493 - PubMed
-
- Black M, Billing BH, Heirwegh KP. (1970) Determination of bilirubin UDP-glucuronyl transferase activity in needle-biopsy specimens of human liver. Clin Chim Acta 29:27–35 - PubMed
-
- Brierley CH, Burchell B. (1993) Human UDP-glucuronosyl transferases: chemical defence, jaundice and gene therapy. Bioessays 15:749–754 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

