Bcl-2 regulates HIF-1alpha protein stabilization in hypoxic melanoma cells via the molecular chaperone HSP90
- PMID: 20668552
- PMCID: PMC2910721
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011772
Bcl-2 regulates HIF-1alpha protein stabilization in hypoxic melanoma cells via the molecular chaperone HSP90
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Bcl-2 Regulates HIF-1α Protein Stabilization in Hypoxic Melanoma Cells via the Molecular Chaperone HSP90.PLoS One. 2022 May 3;17(5):e0268235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268235. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35503789 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 (HIF-1) is a transcription factor that is a critical mediator of the cellular response to hypoxia. Enhanced levels of HIF-1alpha, the oxygen-regulated subunit of HIF-1, is often associated with increased tumour angiogenesis, metastasis, therapeutic resistance and poor prognosis. It is in this context that we previously demonstrated that under hypoxia, bcl-2 protein promotes HIF-1/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-mediated tumour angiogenesis.
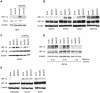
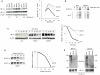
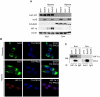
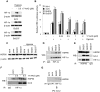
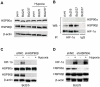
Methodology/principal findings: By using human melanoma cell lines and their stable or transient derivative bcl-2 overexpressing cells, the current study identified HIF-1alpha protein stabilization as a key regulator for the induction of HIF-1 by bcl-2 under hypoxia. We also demonstrated that bcl-2-induced accumulation of HIF-1alpha protein during hypoxia was not due to an increased gene transcription or protein synthesis. In fact, it was related to a modulation of HIF-1alpha protein expression at a post-translational level, indeed its degradation rate was faster in the control lines than in bcl-2 transfectants. The bcl-2-induced HIF-1alpha stabilization in response to low oxygen tension conditions was achieved through the impairment of ubiquitin-dependent HIF-1alpha degradation involving the molecular chaperone HSP90, but it was not dependent on the prolyl hydroxylation of HIF-1alpha protein. We also showed that bcl-2, HIF-1alpha and HSP90 proteins form a tri-complex that may contribute to enhancing the stability of the HIF-1alpha protein in bcl-2 overexpressing clones under hypoxic conditions. Finally, by using genetic and pharmacological approaches we proved that HSP90 is involved in bcl-2-dependent stabilization of HIF-1alpha protein during hypoxia, and in particular the isoform HSP90beta is the main player in this phenomenon.
Conclusions/significance: We identified the stabilization of HIF-1alpha protein as a mechanism through which bcl-2 induces the activation of HIF-1 in hypoxic tumour cells involving the beta isoform of molecular chaperone HSP90.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
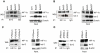
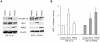
References
-
- Semenza GL. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:721–732. - PubMed
-
- Jeong JW, Bae MK, Ahn MY, Kim SH, Sohn TK, et al. Regulation and destabilization of HIF-1alpha by ARD1-mediated acetylation. Cell. 2002;111:709–720. - PubMed
-
- Cho H, Ahn DR, Park H, Yang EG. Modulation of p300 binding by posttranslational modifications of the C-terminal activation domain of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. FEBS Lett. 2007;581:1542–1548. - PubMed
-
- Bilton R, Trottier E, Pouyssegur J, Brahimi-Horn MC. ARDent about acetylation and deacetylation in hypoxia signalling. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:616–621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

