Diffusion tensor imaging and white matter lesions at the subacute stage in mild traumatic brain injury with persistent neurobehavioral impairment
- PMID: 20669166
- PMCID: PMC6870077
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21092
Diffusion tensor imaging and white matter lesions at the subacute stage in mild traumatic brain injury with persistent neurobehavioral impairment
Abstract
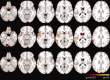
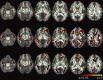
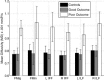
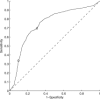
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) can induce long-term behavioral and cognitive disorders. Although the exact origin of these mTBI-related disorders is not known, they may be the consequence of diffuse axonal injury (DAI). Here, we investigated whether MRI at the subacute stage can detect lesions that are associated with poor functional outcome in mTBI by using anatomical images (T(1) ) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). Twenty-three patients with mTBI were investigated and compared with 23 healthy volunteers. All patients underwent an MRI investigation and clinical tests between 7 and 28 days (D15) and between 3 and 4 months (M3) after injury. Patients were divided in two groups of poor outcome (PO) and good outcome (GO), based on their complaints at M3. Groupwise differences in gray matter partial volume between PO patients, GO patients and controls were analyzed using Voxel-Based Morphometry (VBM) from T(1) data at D15. Differences in microstructural architecture were investigated using Tract-Based Spatial Statistics (TBSS) and the diffusion images obtained from DTI data at D15. Permutation-based non-parametric testing was used to assess cluster significance at p < 0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons. Twelve GO patients and 11 PO patients were identified on the basis of their complaints. In PO patients, gray matter partial volume was significantly lower in several cortical and subcortical regions compared with controls, but did not differ from that of GO patients. No difference in diffusion variables was found between GO and controls. PO patients showed significantly higher mean diffusivity values than both controls and GO patients in the corpus callosum, the right anterior thalamic radiations and the superior longitudinal fasciculus, the inferior longitudinal fasciculus and the fronto-occipital fasciculus bilaterally. In conclusion, PO patients differed from GO patients by the presence of diffusion changes in long association white matter fiber tracts but not by gray matter partial volume. These results suggest that DTI at the subacute stage may be a predictive marker of poor outcome in mTBI.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Adams JH,Graham DI,Murray LS,Scott G( 1982): Diffuse axonal injury due to nonmissile head injury in humans: An analysis of 45 cases. Ann Neurol 12: 557–563. - PubMed
-
- Aihara N,Hall J,Pitts L,Fukuda K,Noble L( 1995): Altered immunoexpression of microglia and macrophages after mild head injury. J Neurotrauma 12: 53–63. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J,Friston KJ( 2000): Voxel‐based morphometry—The methods. Neuroimage 11: 805–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

