Characteristics of the sequence effect in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 20669182
- PMCID: PMC4782591
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.23251
Characteristics of the sequence effect in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
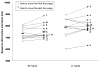
The sequence effect (SE) in Parkinson's disease (PD) is progressive slowing of sequential movements. It is a feature of bradykinesia, but is separate from a general slowness without deterioration over time. It is commonly seen in PD, but its physiology is unclear. We measured general slowness and the SE separately with a computer-based, modified Purdue pegboard in 11 patients with advanced PD. We conducted a placebo-controlled, four-way crossover study to learn whether levodopa and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) could improve general slowness or the SE. We also examined the correlation between the SE and clinical fatigue. Levodopa alone and rTMS alone improved general slowness, but rTMS showed no additive effect on levodopa. Levodopa alone, rTMS alone, and their combination did not alleviate the SE. There was no correlation between the SE and fatigue. This study suggests that dopaminergic dysfunction and abnormal motor cortex excitability are not the relevant mechanisms for the SE. Additionally, the SE is not a component of clinical fatigue. Further work is needed to establish the physiology and clinical relevance of the SE. © 2010 Movement Disorder Society.
Figures



References
-
- Berardelli A, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD, Hallett M. Pathophysiology of bradykinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2001;124:2131–2146. - PubMed
-
- Evarts EV, Teravainen H, Calne DB. Reaction time in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 1981;104:167–186. - PubMed
-
- Velasco F, Velasco M. A quantitative evaluation of the effects of L-dopa on Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology. 1973;12:89–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

