Elevated high sensitive C-reactive protein and apelin levels after percutaneous coronary intervention and drug-eluting stent implantation
- PMID: 20669343
- PMCID: PMC2916086
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1001004
Elevated high sensitive C-reactive protein and apelin levels after percutaneous coronary intervention and drug-eluting stent implantation
Abstract
Objective: Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) triggers an acute inflammatory response, while sirolimus is known to have anti-inflammatory properties; the inflammatory system response to PCI after sirolimus-eluting stent placement remains unclear. The purpose of this study is to determine the changes in high sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and apelin after PCI procedure and drug-eluting stent implantation in patients with and without reduced left ventricular systolic function.
Methods: Forty-eight consecutive patients undergoing PCI at the Beijing Anzhen Hospital between July and September 2006 were recruited. Sirolimus-eluting stents were employed in all patients. Blood samples were drawn immediately before and 24 h after the procedure. Plasma hs-CRP and apelin levels were determined by enzyme immunoassay.
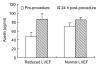
Results: Paired t-test revealed a significant increase in both hs-CRP and apelin post-procedure (P=0.006 and P<0.0001, respectively). Patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) had significantly lower baseline apelin levels compared to those with normal ventricular function [(46.8+/-10.8) vs. (72.0+/-8.4) pg/ml, P<0.001]. However, apelin increased to a level similar to the level of those with normal left ventricular systolic function 24 h after the PCI procedure [(86.7+/-11.6) vs. (85.1+/-6.1) pg/ml, P=0.72].
Conclusions: hs-CRP and apelin levels increased after PCI and sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Patients with impaired left ventricular systolic function had significantly lower baseline apelin levels, which increased significantly after PCI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic values of C-reactive protein levels on clinical outcome after implantation of sirolimus-eluting stents in patients on hemodialysis.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2009 Dec;2(6):513-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.109.889915. Epub 2009 Oct 13. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2009. PMID: 20031768
-
Effects of drug-eluting stents on systemic inflammatory response in patients with unstable angina pectoris undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.Heart Vessels. 2008 Mar;23(2):75-82. doi: 10.1007/s00380-007-1020-y. Epub 2008 Apr 4. Heart Vessels. 2008. PMID: 18389330 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of inflammatory markers and angiographic outcomes after implantation of sirolimus and paclitaxel-eluting stents.Heart. 2009 Jun;95(12):970-5. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2008.153114. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Heart. 2009. PMID: 18772180 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of changes in early inflammatory markers between sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stent implantation.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2009 Apr;23(2):137-43. doi: 10.1007/s10557-008-6149-0. Epub 2008 Nov 19. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2009. PMID: 19016317 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of direct sirolimus-eluting stent implantation on the early systemic inflammatory response compared with complementary stent implantation.Coron Artery Dis. 2009 Jan;20(1):65-70. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0b013e32830d27bd. Coron Artery Dis. 2009. PMID: 19018239 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Differential Gene Expression in Coiled versus Flow-Diverter-Treated Aneurysms: RNA Sequencing Analysis in a Rabbit Aneurysm Model.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016 Jun;37(6):1114-21. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4648. Epub 2015 Dec 31. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016. PMID: 26721773 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

