Severe thrombocytopenia with iron deficiency anemia
- PMID: 20670168
- PMCID: PMC3439835
- DOI: 10.3109/08880011003739455
Severe thrombocytopenia with iron deficiency anemia
Abstract
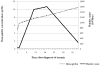
Although severe thrombocytopenia has been reported among children with iron deficiency anemia, the presence of both anemia and thrombocytopenia can suggest serious or malignant bone marrow dysfunction, requiring further work-up. This paper reviews the management and outcomes of patients with the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia presenting with severe thrombocytopenia. The authors present 4 pediatric patients with iron deficiency anemia and severe thrombocytopenia at initial presentation. Charts were reviewed after approval by the institutional review boards at both St. Jude Children's Research Hospital and LeBonheur Children's Medical Center in Memphis, Tennessee. All 4 patients' hemoglobin concentrations and platelet counts normalized within 1 to 3 weeks of initiating iron supplementation, suggesting that in such patients iron supplementation can obviate the need for invasive diagnostic procedures. In addition, these patients all had a platelet "overshoot" phenomenon during iron therapy prior to normalization of platelet counts, the mechanism of which is still unknown. The literature exploring the mechanism behind the current clinical findings is reviewed.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest: There are no potential conflicts of interests for any of the authors to report. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Sherry B, Bister D, Yip R. Continuation of decline in prevalence of anemia in low-income children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1997;151:928–930. - PubMed
-
- Oski FA. Iron deficiency in infancy and childhood. New Engl J Med. 1993;29:190–193. - PubMed
-
- Kasper CK, Whissell DY, Wallerstein CO. Clinical aspects of iron deficiency Anemia. JAMA. 1965;191:359–363. - PubMed
-
- Sandoval C, Berger E, Ozkaynak MF, et al. Severe iron deficiency anemia in forty-two pediatric patients. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2002;19:157–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA-78224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM061393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA-60419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-36401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA060419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-21765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA051001/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA036401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA51001/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM-61393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA060419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA078224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA036401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources