Microarray-driven validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in a rat vocal fold model of mucosal injury
- PMID: 20670610
- PMCID: PMC2951325
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2010.07.021
Microarray-driven validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in a rat vocal fold model of mucosal injury
Abstract
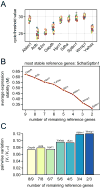
Relative quantification by normalization against a stably expressed reference gene is a widely used data analysis method in microarray and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) platforms; however, recent evidence suggests that many commonly utilized reference genes are unstable in certain experimental systems and situations. The primary aim of this study, therefore, was to screen and identify stably expressed reference genes in a well-established rat model of vocal fold mucosal injury. We selected and evaluated the expression stability of nine candidate reference genes. Ablim1, Sptbn1, and Wrnip1 were identified as stably expressed in a model-specific microarray dataset and were further validated as suitable reference genes in an independent qRT-PCR experiment using 2(-DeltaCT) and pairwise comparison-based (geNorm) analyses. Parallel analysis of six commonly used reference genes identified Sdha as the only stably expressed candidate in this group. Sdha, Sptbn1, and the geometric mean of Sdha and Sptbn1 each provided accurate normalization of target gene Tgfb1; Gapdh, the least stable candidate gene in our dataset, provided inaccurate normalization and an invalid experimental result. The stable reference genes identified here are suitable for accurate normalization of target gene expression in vocal fold mucosal injury experiments.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

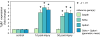
References
-
- Huggett J, Dheda K, Bustin S, Zumla A. Real-time RT-PCR normalisation; strategies and considerations. Genes Immun. 2005;6:279–84. - PubMed
-
- Winer J, Jung CK, Shackel I, Williams PM. Development and validation of real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for monitoring gene expression in cardiac myocytes in vitro. Anal Biochem. 1999;270:41–9. - PubMed
-
- Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8. - PubMed
-
- Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA, Mills AG, Gorn V, Singer MJ, Reed MW. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction to study mRNA decay: comparison of endpoint and real-time methods. Anal Biochem. 2000;285:194–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

