Extracellular matrix roles during cardiac repair
- PMID: 20670633
- PMCID: PMC2946433
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.07.010
Extracellular matrix roles during cardiac repair
Abstract
The cardiac extracellular matrix (ECM) provides a platform for cells to maintain structure and function, which in turn maintains tissue function. In response to injury, the ECM undergoes remodeling that involves synthesis, incorporation, and degradation of matrix proteins, with the net outcome determined by the balance of these processes. The major goals of this review are a) to serve as an initial resource for students and investigators new to the cardiac ECM remodeling field, and b) to highlight a few of the key exciting avenues and methodologies that have recently been explored. While we focus on cardiac injury and responses of the left ventricle (LV), the mechanisms reviewed here have pathways in common with other wound healing models.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
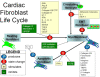
References
-
- Adair-Kirk TL, Atkinson JJ, Broekelmann TJ, Doi M, Tryggvason K, Miner JH, Mecham RP, Senior RM. A Site on Laminin {alpha}5, AQARSAASKVKVSMKF, Induces Inflammatory Cell Production of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 and Chemotaxis. J Immunol. 2003;171(1):398–406. - PubMed
-
- Ali MA, Schulz R. Activation of MMP-2 as a key event in oxidative stress injury to the heart. Front Biosci. 2009;14:699–716. - PubMed
-
- Bishop JE, Laurent GJ. Collagen turnover and its regulation in the normal and hypertrophying heart. Eur Heart J 16 Suppl C. 1995:38–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

