Diet choice, cortisol reactivity, and emotional feeding in socially housed rhesus monkeys
- PMID: 20670639
- PMCID: PMC2949469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.07.010
Diet choice, cortisol reactivity, and emotional feeding in socially housed rhesus monkeys
Abstract
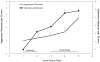
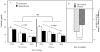
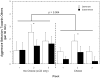
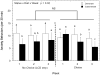
Chronic psychosocial stress produces an array of adverse health consequences that are highly comorbid, including emotional eating, affective disorders, and metabolic syndrome. The consumption of high caloric diets (HCDs) is thought to provide comfort in the face of unrelenting psychosocial stress. Using social subordination in female rhesus monkeys as a model of continual exposure to daily stressors in women, we tested the hypothesis that subordinate females would consume significantly more calories from a HCD compared to dominant females, and this pattern of food intake would be associated with reduced cortisol release and reduced frequency of anxiety-like behaviors. Food intake, parameters of cortisol secretion, and socio-emotional behavior were assessed for 3 weeks during a no choice phase when only a low caloric diet (LCD) was available and during a choice condition when both a LCD and HCD were available. While all animals preferred the HCD, subordinate females consumed significantly more of the HCD than did dominant females. A flattening of the diurnal cortisol rhythm and a greater increase in serum cortisol to an acute social separation occurred during the diet choice condition in all females. Furthermore, the rate of anxiety-like behavior progressively declined during the 3-week choice condition in subordinate but not dominant females. These data provide support for the hypothesis that daily exposure to psychosocial stress increases consumption of calorically dense foods. Furthermore, consumption of HCDs may be a metabolic stressor that synergizes with the psychosocial stress of subordination to further increase the consumption of these diets.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- McEwen BS. Stress, adaptation, and disease. Allostasis and allostatic load. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;840:33–44. - PubMed
-
- Schulkin J, Gold PW, McEwen BS. Induction of corticotropin-releasing hormone gene expression by glucocorticoids: implication for understanding the states of fear and anxiety and allostatic load. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1998;23:219–43. - PubMed
-
- Swaab DF, Bao AM, Lucassen PJ. The stress system in the human brain in depression and neurodegeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2005 - PubMed
-
- Holsboer F. Stress, hypercortisolism and corticosteroid receptors in depression: implications for therapy. J Affect Disord. 2001;62:77–91. - PubMed
-
- Lo Sauro C, Ravaldi C, Cabras PL, Faravelli C, Ricca V. Stress, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and eating disorders. Neuropsychobiology. 2008;57:95–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

