Defining the pathway of cytoplasmic maturation of the 60S ribosomal subunit
- PMID: 20670889
- PMCID: PMC2925414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.06.018
Defining the pathway of cytoplasmic maturation of the 60S ribosomal subunit
Abstract
In eukaryotic cells the final maturation of ribosomes occurs in the cytoplasm, where trans-acting factors are removed and critical ribosomal proteins are added for functionality. Here, we have carried out a comprehensive analysis of cytoplasmic maturation, ordering the known steps into a coherent pathway. Maturation is initiated by the ATPase Drg1. Downstream, assembly of the ribosome stalk is essential for the release of Tif6. The stalk recruits GTPases during translation. Because the GTPase Efl1, which is required for the release of Tif6, resembles the translation elongation factor eEF2, we suggest that assembly of the stalk recruits Efl1, triggering a step in 60S biogenesis that mimics aspects of translocation. Efl1 could thereby provide a mechanism to functionally check the nascent subunit. Finally, the release of Tif6 is a prerequisite for the release of the nuclear export adaptor Nmd3. Establishing this pathway provides an important conceptual framework for understanding ribosome maturation.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


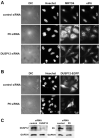
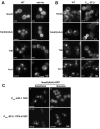
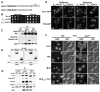
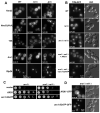
References
-
- Becam AM, Nasr F, Racki WJ, Zagulski M, Herbert CJ. Ria1p (Ynl163c), a protein similar to elongation factors 2, is involved in the biogenesis of the 60S subunit of the ribosome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Genet Genomics. 2001;266:454–462. - PubMed
-
- Berk V, Cate JH. Insights into protein biosynthesis from structures of bacterial ribosomes. Current opinion in structural biology. 2007;17:302–309. - PubMed
-
- Bradatsch B, Katahira J, Kowalinski E, Bange G, Yao W, Sekimoto T, Baumgartel V, Boese G, Bassler J, Wild K, et al. Arx1 functions as an unorthodox nuclear export receptor for the 60S preribosomal subunit. Molecular cell. 2007;27:767–779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

