A two-parameter generalized Poisson model to improve the analysis of RNA-seq data
- PMID: 20671027
- PMCID: PMC2943596
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq670
A two-parameter generalized Poisson model to improve the analysis of RNA-seq data
Abstract
Deep sequencing of RNAs (RNA-seq) has been a useful tool to characterize and quantify transcriptomes. However, there are significant challenges in the analysis of RNA-seq data, such as how to separate signals from sequencing bias and how to perform reasonable normalization. Here, we focus on a fundamental question in RNA-seq analysis: the distribution of the position-level read counts. Specifically, we propose a two-parameter generalized Poisson (GP) model to the position-level read counts. We show that the GP model fits the data much better than the traditional Poisson model. Based on the GP model, we can better estimate gene or exon expression, perform a more reasonable normalization across different samples, and improve the identification of differentially expressed genes and the identification of differentially spliced exons. The usefulness of the GP model is demonstrated by applications to multiple RNA-seq data sets.
Figures
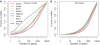
 for the Poisson model (A) or
for the Poisson model (A) or  for the GP model (B). Then the percentage of mRNA amount contributed from the top 1, 10,…, 10 000 genes was calculated and plotted.
for the GP model (B). Then the percentage of mRNA amount contributed from the top 1, 10,…, 10 000 genes was calculated and plotted.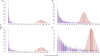
 ) were about 677 476, 329 818, 277 529 and 272 551. And the total number of estimated reads from the GP model (
) were about 677 476, 329 818, 277 529 and 272 551. And the total number of estimated reads from the GP model ( ) were about 6340.2, 11297.0, 4589.7 and 9138.9 for these four genes.
) were about 6340.2, 11297.0, 4589.7 and 9138.9 for these four genes.
Similar articles
-
deGPS is a powerful tool for detecting differential expression in RNA-sequencing studies.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jun 13;16(1):455. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1676-0. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26070955 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying differentially spliced genes from two groups of RNA-seq samples.Gene. 2013 Apr 10;518(1):164-70. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.11.045. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23228854
-
Differential expression analysis of RNA sequencing data by incorporating non-exonic mapped reads.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):S14. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S7-S14. Epub 2015 Jun 11. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26099631 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics.Nat Rev Genet. 2009 Jan;10(1):57-63. doi: 10.1038/nrg2484. Nat Rev Genet. 2009. PMID: 19015660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of available methods for diverse RNA-Seq data analyses.Sci China Life Sci. 2011 Dec;54(12):1121-8. doi: 10.1007/s11427-011-4255-x. Epub 2012 Jan 7. Sci China Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 22227904 Review.
Cited by
-
Poisson factor models with applications to non-normalized microRNA profiling.Bioinformatics. 2013 May 1;29(9):1105-11. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt091. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23428639 Free PMC article.
-
A new approach to bias correction in RNA-Seq.Bioinformatics. 2012 Apr 1;28(7):921-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts055. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22285831 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in estimating percent inclusion of alternatively spliced junctions from RNA-seq data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Apr 19;13 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):S11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-S6-S11. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22537040 Free PMC article.
-
deGPS is a powerful tool for detecting differential expression in RNA-sequencing studies.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jun 13;16(1):455. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1676-0. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26070955 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and comparison of human nuclear and cytosolic editomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 16;110(29):E2741-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218884110. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23818636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cloonan N, Forrest AR, Kolle G, Gardiner BB, Faulkner GJ, Brown MK, Taylor DF, Steptoe AL, Wani S, Bethel G, et al. Stem cell transcriptome profiling via massive-scale mRNA sequencing. Nat. Methods. 2008;5:613–619. - PubMed
-
- Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods. 2008;5:621–628. - PubMed

