A two-parameter generalized Poisson model to improve the analysis of RNA-seq data
- PMID: 20671027
- PMCID: PMC2943596
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq670
A two-parameter generalized Poisson model to improve the analysis of RNA-seq data
Abstract
Deep sequencing of RNAs (RNA-seq) has been a useful tool to characterize and quantify transcriptomes. However, there are significant challenges in the analysis of RNA-seq data, such as how to separate signals from sequencing bias and how to perform reasonable normalization. Here, we focus on a fundamental question in RNA-seq analysis: the distribution of the position-level read counts. Specifically, we propose a two-parameter generalized Poisson (GP) model to the position-level read counts. We show that the GP model fits the data much better than the traditional Poisson model. Based on the GP model, we can better estimate gene or exon expression, perform a more reasonable normalization across different samples, and improve the identification of differentially expressed genes and the identification of differentially spliced exons. The usefulness of the GP model is demonstrated by applications to multiple RNA-seq data sets.
Figures
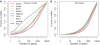
 for the Poisson model (A) or
for the Poisson model (A) or  for the GP model (B). Then the percentage of mRNA amount contributed from the top 1, 10,…, 10 000 genes was calculated and plotted.
for the GP model (B). Then the percentage of mRNA amount contributed from the top 1, 10,…, 10 000 genes was calculated and plotted.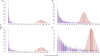
 ) were about 677 476, 329 818, 277 529 and 272 551. And the total number of estimated reads from the GP model (
) were about 677 476, 329 818, 277 529 and 272 551. And the total number of estimated reads from the GP model ( ) were about 6340.2, 11297.0, 4589.7 and 9138.9 for these four genes.
) were about 6340.2, 11297.0, 4589.7 and 9138.9 for these four genes.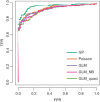
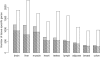
References
-
- Cloonan N, Forrest AR, Kolle G, Gardiner BB, Faulkner GJ, Brown MK, Taylor DF, Steptoe AL, Wani S, Bethel G, et al. Stem cell transcriptome profiling via massive-scale mRNA sequencing. Nat. Methods. 2008;5:613–619. - PubMed
-
- Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods. 2008;5:621–628. - PubMed

