Urine proteome analysis may allow noninvasive differential diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 20671095
- PMCID: PMC2963504
- DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0345
Urine proteome analysis may allow noninvasive differential diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
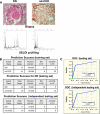
Objective: Chronic renal insufficiency and/or proteinuria in type 2 diabetes may stem from chronic renal diseases (CKD) other than classic diabetic nephropathy in more than one-third of patients. We interrogated urine proteomic profiles generated by surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization-time of flight/mass spectrometry with the aim of isolating a set of biomarkers able to reliably identify biopsy-proven diabetic nephropathy and to establish a stringent correlation with the different patterns of renal injury.
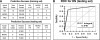
Research design and methods: Ten micrograms of urine proteins from 190 subjects (20 healthy subjects, 20 normoalbuminuric, and 18 microalbuminuric diabetic patients and 132 patients with biopsy-proven nephropathy: 65 diabetic nephropathy, 10 diabetic with nondiabetic CKD [nd-CKD], and 57 nondiabetic with CKD) were run using a CM10 ProteinChip array and analyzed by supervised learning methods (Classification and Regression Tree analysis).
Results: The classification model correctly identified 75% of patients with normoalbuminuria, 87.5% of those with microalbuminuria, and 87.5% of those with diabetic nephropathy when applied to a blinded testing set. Most importantly, it was able to reliably differentiate diabetic nephropathy from nd-CKD in both diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Among the best predictors of the classification model, we identified and validated two proteins, ubiquitin and β2-microglobulin.
Conclusions: Our data suggest the presence of a specific urine proteomic signature able to reliably identify type 2 diabetic patients with diabetic glomerulosclerosis.
Figures

References
-
- U.S. Renal Data System. USRDS 2009 Annual Data Report. Bethesda, MD, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2009
-
- Colantonio DA, Chan DW. The clinical application of proteomics. Clin Chim Acta 2005;357:151–158 - PubMed
-
- Mazzucco G, Bertani T, Fortunato M, Bernardi M, Leutner M, Boldorini R, Monga G. Different patterns of renal damage in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a multicentric study on 393 biopsies. Am J Kidney Dis 2002;39:713–720 - PubMed
-
- Thongboonkerd V. Searching for novel biomarkers and new therapeutic targets of diabetic nephropathy using proteomics approaches. Contrib Nephrol 2008;160:37–52 - PubMed
-
- Merchant ML, Klein JB. Proteomics and diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 2007;27:627–636 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

