A novel latent membrane 2 transcript expressed in Epstein-Barr virus-positive NK- and T-cell lymphoproliferative disease encodes a target for cellular immunotherapy
- PMID: 20671118
- PMCID: PMC2981530
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-292268
A novel latent membrane 2 transcript expressed in Epstein-Barr virus-positive NK- and T-cell lymphoproliferative disease encodes a target for cellular immunotherapy
Abstract
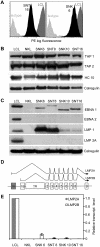
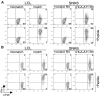
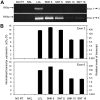
Therapeutic targeting of virus-encoded proteins using cellular immunotherapy has proved successful for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease. However, the more limited repertoire and immunogenicity of EBV-encoded proteins in other malignancies such as Hodgkin lymphoma and extranodal natural killer (NK)/T lymphoma has been more challenging to target. The immunosubdominant latent membrane protein 2 (LMP2) is considered the optimal target in such Latency II tumors, although data relating to its expression in T/NK malignancies are limited. In addressing the validity of LMP2 as an immunotherapeutic target we found that LMP2-specific effector CD8(+) T cells recognized and killed EBV-positive NK- and T-cell tumor lines, despite an apparent absence of LMP2A protein and barely detectable levels of LMP2 transcripts from the conventional LMP2A and LMP2B promoters. We resolved this paradox by identifying in these lines a novel LMP2 mRNA, initiated from within the EBV terminal repeats and containing downstream, epitope-encoding exons. This same mRNA was also highly expressed in primary (extra-nodal) NK/T lymphoma tissue, with virtually undetectable levels of conventional LMP2A/B transcripts. Expression of this novel transcript in T/NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases validates LMP2 as an attractive target for cellular immunotherapy and implicates this truncated LMP2 protein in NK- and T-cell lymphomagenesis. This study is registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00062868.
Figures
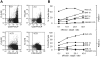

Comment in
-
Mystery of the missing target.Blood. 2010 Nov 11;116(19):3691-2. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-300590. Blood. 2010. PMID: 21071613 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rickinson AB, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. 5th Ed. Vol 2. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2655–2700.
-
- Roskrow MA, Suzuki N, Gan YJ, et al. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes for the treatment of patients with EBV-positiye relapsed Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1998;91(8):2925–2934. - PubMed
-
- Bollard CM, Straathof KC, Huls MH, et al. The generation and characterization of LMP2-specific CTLs for use as adoptive transfer from patients with relapsed EBV-positive Hodgkin disease. J Immunother. 2004;27(4):317–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

