Identification of a cell of origin for human prostate cancer
- PMID: 20671189
- PMCID: PMC2917982
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1189992
Identification of a cell of origin for human prostate cancer
Abstract
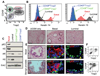
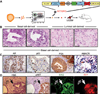
Luminal cells are believed to be the cells of origin for human prostate cancer, because the disease is characterized by luminal cell expansion and the absence of basal cells. Yet functional studies addressing the origin of human prostate cancer have not previously been reported because of a lack of relevant in vivo human models. Here we show that basal cells from primary benign human prostate tissue can initiate prostate cancer in immunodeficient mice. The cooperative effects of AKT, ERG, and androgen receptor in basal cells recapitulated the histological and molecular features of human prostate cancer, with loss of basal cells and expansion of luminal cells expressing prostate-specific antigen and alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase. Our results demonstrate that histological characterization of cancers does not necessarily correlate with the cellular origins of the disease.
Figures

Comment in
-
Tumorigenesis: Ground zero.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Sep;10(9):598. doi: 10.1038/nrc2923. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20803808 No abstract available.
-
Prostate cancer from basal cells.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010 Oct;7(10):550. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.146. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20922829 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

