Albuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate independently associate with acute kidney injury
- PMID: 20671214
- PMCID: PMC3013549
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010010128
Albuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate independently associate with acute kidney injury
Abstract
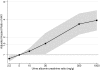
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is increasingly common and a significant contributor to excess death in hospitalized patients. CKD is an established risk factor for AKI; however, the independent graded association of urine albumin excretion with AKI is unknown. We analyzed a prospective cohort of 11,200 participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study for the association between baseline urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio and estimated GFR (eGFR) with hospitalizations or death with AKI. The incidence of AKI events was 4.0 per 1000 person-years of follow-up. Using participants with urine albumin-to-creatinine ratios <10 mg/g as a reference, the relative hazards of AKI, adjusted for age, gender, race, cardiovascular risk factors, and categories of eGFR were 1.9 (95% CI, 1.4 to 2.6), 2.2 (95% CI, 1.6 to 3.0), and 4.8 (95% CI, 3.2 to 7.2) for urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio groups of 11 to 29 mg/g, 30 to 299 mg/g, and ≥300 mg/g, respectively. Similarly, the overall adjusted relative hazard of AKI increased with decreasing eGFR. Patterns persisted within subgroups of age, race, and gender. In summary, albuminuria and eGFR have strong, independent associations with incident AKI.
Figures


Comment in
-
Quantifying severity of chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for acute kidney injury.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Oct;21(10):1602-4. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010080816. Epub 2010 Sep 9. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20829406 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hou SH, Bushinsky DA, Wish JB, Cohen JJ, Harrington JT: Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency: A prospective study. Am J Med 74: 243–248, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Shusterman N, Strom BL, Murray TG, Morrison G, West SL, Maislin G: Risk factors and outcome of hospital-acquired acute renal failure. Clinical Epidemiologic Study. Am J Med 83: 65–71, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Liano F, Pascual J: Epidemiology of acute renal failure: A prospective, multicenter, community-based study. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney Int 50: 811–818, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Levy EM, Viscoli CM, Horwitz RI: The effect of acute renal failure on mortality. A cohort analysis. JAMA 275: 1489–1494, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC055016/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055019/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55021/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55019/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55015/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55020/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55018/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55022/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55016/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

