Histopathological image analysis: a review
- PMID: 20671804
- PMCID: PMC2910932
- DOI: 10.1109/RBME.2009.2034865
Histopathological image analysis: a review
Abstract
Over the past decade, dramatic increases in computational power and improvement in image analysis algorithms have allowed the development of powerful computer-assisted analytical approaches to radiological data. With the recent advent of whole slide digital scanners, tissue histopathology slides can now be digitized and stored in digital image form. Consequently, digitized tissue histopathology has now become amenable to the application of computerized image analysis and machine learning techniques. Analogous to the role of computer-assisted diagnosis (CAD) algorithms in medical imaging to complement the opinion of a radiologist, CAD algorithms have begun to be developed for disease detection, diagnosis, and prognosis prediction to complement the opinion of the pathologist. In this paper, we review the recent state of the art CAD technology for digitized histopathology. This paper also briefly describes the development and application of novel image analysis technology for a few specific histopathology related problems being pursued in the United States and Europe.
Keywords: computer-assisted interpretation; histopathology; image analysis; microscopy analysis.
Figures



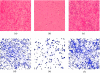
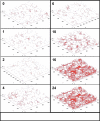

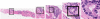

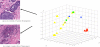


References
-
- Mendez AJ, Tahoces PG, Lado MJ, Souto M, Vidal JJ. Computer-aided diagnosis: automatic detection of malignant masses in digitized mammograms. Med Phys. 1998 Jun;25:957–64. - PubMed
-
- Tang J, Rangayyan R, Xu J, El Naqa I, Yang Y. Computer-Aided Detection and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer with Mammography: Recent Advances. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2009 Jan 20; - PubMed
-
- Rubin R, Strayer D, Rubin E, McDonald J. Rubin's pathology: clinicopathologic foundations of medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
-
- Weind KL, Maier CF, Rutt BK, Moussa M. Invasive carcinomas and fibroadenomas of the breast: comparison of microvessel distributions--implications for imaging modalities. Radiology. 1998 Aug;208:477–83. - PubMed
-
- Bartels PH, Thompson D, Bibbo M, Weber JE. Bayesian belief networks in quantitative histopathology. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 1992 Dec;14:459–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R03CA128081-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136535/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21CA127186-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA127186/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA136535-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ARRA-NCL-3 21CA127186-02S1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03CA143991-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA128081/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM010119/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134451/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA143991/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01LM010119/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

