Loop Electrosurgical Excisional Procedure (LEEP) Done for Discrepancy: Does the Time from HGSIL Affect Pathologic Grade of CIN in LEEP Specimen?
- PMID: 20671925
- PMCID: PMC2910507
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/743097
Loop Electrosurgical Excisional Procedure (LEEP) Done for Discrepancy: Does the Time from HGSIL Affect Pathologic Grade of CIN in LEEP Specimen?
Abstract
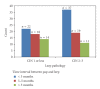
Objective. When pathologic discrepancy arises between high-grade cytology on Papanicolaou (Pap) smear and low-grade histology on cervical biopsy, Loop Electrosurgical Excisional Procedure (LEEP) is one management alternative. Our objective was to determine whether the time from initial HGSIL Pap to LEEP affects the pathologic grade of the LEEP specimen. Study Design. We performed a retrospective case-control study identifying LEEPs performed for discrepancy over a 10-year period (1997-2007). 121 subjects were separated into two groups based on LEEP pathology (</=CIN 1 and CIN 2,3) and compared using chi(2). Results. Of the 121 LEEP specimens, 67 (55.4%) had CIN 2,3. CIN 2,3 was more often discovered when LEEP was performed within 3 months of the HGSIL Pap smear versus after 5 months (55.2% versus 16.4%, P = .096). Conclusion. Women undergoing LEEP for discrepancy >5 months from their HGSIL Pap demonstrated a trend toward less CIN 2,3 on LEEP pathology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of loop electrosurgical excision procedure with cold coagulation for treating cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: A two center cohort study.Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2017 Mar;60(2):200-206. doi: 10.5468/ogs.2017.60.2.200. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28344962 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Immediate Loop Electrode Excisional Procedure for High-Grade Cervical Cytology in an Urban Academic Clinic Setting.J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2018 Oct;22(4):311-313. doi: 10.1097/LGT.0000000000000426. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2018. PMID: 30106814
-
The accuracy of cervical cancer and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia diagnosis with loop electrosurgical excisional procedure under colposcopic vision.J Gynecol Oncol. 2009 Mar;20(1):35-8. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2009.20.1.35. Epub 2009 Mar 31. J Gynecol Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19471663 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of concordance between loop electrosurgical excisional procedure and cervical colposcopic biopsy results.J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2024 Mar 6;25(1):13-17. doi: 10.4274/jtgga.galenos.2023.2023-1-11. Epub 2023 Dec 6. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38054754 Free PMC article.
-
High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion in inmates from Ohio: cervical screening and biopsy follow-up.Cytojournal. 2006 May 10;3:15. doi: 10.1186/1742-6413-3-15. Cytojournal. 2006. PMID: 16686955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Massad LS, Collins YC, Meyer PM. Biopsy correlates of abnormal cervical cytology classified using the bethesda system. Gynecologic Oncology. 2001;82(3):516–522. - PubMed
-
- Wright TC, Jr., Cox JT, Massad LS, Twiggs LB, Wilkinson EJ. 2001 consensus guidelines for the management of women with cervical cytological abnormalities. Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease. 2002;6(2):127–143. - PubMed
-
- Wright TC, Jr., Massad LS, Dunton CJ, Spitzer M, Wilkinson EJ, Solomon D. 2006 Consensus guidelines for the management of women with abnormal cervical screening tests. Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease. 2007;11(4):201–222. - PubMed
-
- Melnikow J, Nuovo J, Willan AR, Chan BKS, Howell LP. Natural history of cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions: a meta- analysis. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1998;92(4):727–735. - PubMed
-
- Moscicki A-B, Schiffman M, Kjaer S, Villa LL. Chapter 5: updating the natural history of HPV and anogenital cancer. Vaccine. 2006;24(3):S42–S51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

