The structure and function of serum opacity factor: a unique streptococcal virulence determinant that targets high-density lipoproteins
- PMID: 20671930
- PMCID: PMC2910554
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/956071
The structure and function of serum opacity factor: a unique streptococcal virulence determinant that targets high-density lipoproteins
Abstract
Serum opacity factor (SOF) is a virulence determinant expressed by a variety of streptococcal and staphylococcal species including both human and animal pathogens. SOF derives its name from its ability to opacify serum where it targets and disrupts the structure of high-density lipoproteins resulting in formation of large lipid vesicles that cause the serum to become cloudy. SOF is a multifunctional protein and in addition to its opacification activity, it binds to a number of host proteins that mediate adhesion of streptococci to host cells, and it plays a role in resistance to phagocytosis in human blood. This article will provide an overview of the structure and function of SOF, its role in the pathogenesis of streptococcal infections, its vaccine potential, its prevalence and distribution in bacteria, and the molecular mechanism whereby SOF opacifies serum and how an understanding of this mechanism may lead to therapies for reducing high-cholesterol concentrations in blood, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Figures



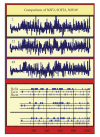

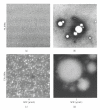

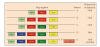

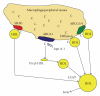
Similar articles
-
Serum opacity factor, a streptococcal virulence factor that binds to apolipoproteins A-I and A-II and disrupts high density lipoprotein structure.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 3;281(9):5515-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512538200. Epub 2006 Jan 3. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16407233
-
Opacity factor activity and epithelial cell binding by the serum opacity factor protein of Streptococcus pyogenes are functionally discrete.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 7;283(10):6359-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706739200. Epub 2008 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18180300
-
Serum opacity factor is a major fibronectin-binding protein and a virulence determinant of M type 2 Streptococcus pyogenes.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Apr;32(1):89-98. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01328.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10216862
-
Streptococcal adhesion and colonization.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1997;8(2):175-200. doi: 10.1177/10454411970080020601. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1997. PMID: 9167092 Review.
-
Genomic organization, structure, regulation and pathogenic role of pilus constituents in major pathogenic Streptococci and Enterococci.Int J Med Microbiol. 2011 Mar;301(3):240-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2010.09.003. Epub 2010 Nov 26. Int J Med Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21112248 Review.
Cited by
-
Virulence factors of Streptococcus anginosus - a molecular perspective.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 26;13:1025136. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1025136. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36386673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomics in serum and culture medium reveal shared and differential gene regulation in pathogenic and commensal Streptococcus suis.Microb Genom. 2023 Apr;9(4):mgen000992. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000992. Microb Genom. 2023. PMID: 37103997 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E mediates enhanced plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol clearance by low-dose streptococcal serum opacity factor via hepatic low-density lipoprotein receptors in vivo.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Aug;31(8):1834-41. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.224360. Epub 2011 May 19. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21597008 Free PMC article.
-
Population and Whole Genome Sequence Based Characterization of Invasive Group A Streptococci Recovered in the United States during 2015.mBio. 2017 Sep 19;8(5):e01422-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01422-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28928212 Free PMC article.
-
Opacification Domain of Serum Opacity Factor Inhibits Beta-Hemolysis and Contributes to Virulence of Streptococcus pyogenes.mSphere. 2017 Apr 19;2(2):e00147-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphereDirect.00147-17. eCollection 2017 Mar-Apr. mSphere. 2017. PMID: 28435893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ward HK, Rudd GV. Studies on haemolytic streptococci from human sources. Australian Journal of Experimental Biology & Medical Science. 1938;16:181–192.
-
- Rowen R, Martin J. Enhancement of cholesterol esterification in serum by an extract of group-A streptococcus. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1963;70:396–405. - PubMed
-
- Saravani GA, Martin DR. Opacity factor from group A streptococci is an apoproteinase. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 1990;68(1-2):35–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

