Serum Interleukin-4 and Total Immunoglobulin E in Nonatopic Alopecia Areata Patients and HLA-DRB1 Typing
- PMID: 20671941
- PMCID: PMC2910459
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/503587
Serum Interleukin-4 and Total Immunoglobulin E in Nonatopic Alopecia Areata Patients and HLA-DRB1 Typing
Abstract
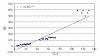
Background. Interleukin-4 (IL-4), a Th(2) cytokine, can stimulate immunoglobulin E (IgE) transcription. No previous studies evaluated the genetic mechanisms in nonatopic AA patients with elevated serum IgE. Objective. To compare serum IL-4 and total IgE levels between Egyptian nonatopic AA patients and healthy subjects and to investigate a possible relation to HLA-DRB1 alleles. Results. Serum IL-4 and total IgE were measured by ELISA in 40 controls and 54 nonatopic AA patients. Patients' HLA-DRB1 typing by sequence specific oligonucleotide probe technique was compared to normal Egyptian population. We found significantly elevated serum IL-4 and total IgE in AA patients (particularly alopecia universalis, AU, and chronic patients) (P < .01). HLA-DRB1*11 is a general susceptibility/chronicity allele. DRB1*13 is a protective allele. DRB1*01 and DRB1*07 are linked to chronicity. Localized AA showed decreased DRB1*03 and DRB1*07. Extensive forms showed increased DRB1*08 and decreased DRB1*04. Elevated IL4 and IgE were observed in patients with DRB1*07 and DRB1*11 not DRB1*04. Conclusion. Serum IL-4 and IgE are elevated in nonatopic AA patients, particularly AU and chronic disease. Relevant susceptibility, chronicity, and severity HLADRB1 alleles may have a role in determining type, magnitude, and duration of immune response in AA favouring increased IL4 and IgE.
Figures
References
-
- Madani S, Shapiro J. Alopecia areata update. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2000;42(4):549–570. - PubMed
-
- Papadopoulos AJ, Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Alopecia areata: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 2000;1(2):101–105. - PubMed
-
- Hedstrand H, Perheentupa J, Ekwall O, et al. Antibodies against hair follicles are associated with alopecia totalis in autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1999;113(6):1054–1058. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann R, Wenzel E, Huth A, et al. Cytokine mRNA levels in alopecia areata before and after treatment with the contact allergen diphenylcyclopropenone. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1994;103(4):530–533. - PubMed
-
- Teraki Y, Imanishi K, Shiohara T. Cytokines in alopecia areata: contrasting cytokine profiles in localized form and extensive form (alopecia universalis) Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 1996;76(6):421–423. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials