Desmosomal molecules in and out of adhering junctions: normal and diseased States of epidermal, cardiac and mesenchymally derived cells
- PMID: 20671973
- PMCID: PMC2909724
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/139167
Desmosomal molecules in and out of adhering junctions: normal and diseased States of epidermal, cardiac and mesenchymally derived cells
Abstract
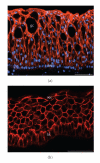
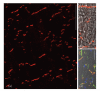
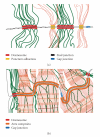
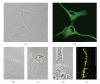
Current cell biology textbooks mention only two kinds of cell-to-cell adhering junctions coated with the cytoplasmic plaques: the desmosomes (maculae adhaerentes), anchoring intermediate-sized filaments (IFs), and the actin microfilament-anchoring adherens junctions (AJs), including both punctate (puncta adhaerentia) and elongate (fasciae adhaerentes) structures. In addition, however, a series of other junction types has been identified and characterized which contain desmosomal molecules but do not fit the definition of desmosomes. Of these special cell-cell junctions containing desmosomal glycoproteins or proteins we review the composite junctions (areae compositae) connecting the cardiomyocytes of mature mammalian hearts and their importance in relation to human arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathies. We also emphasize the various plakophilin-2-positive plaques in AJs (coniunctiones adhaerentes) connecting proliferatively active mesenchymally-derived cells, including interstitial cells of the heart and several soft tissue tumor cell types. Moreover, desmoplakin has also been recognized as a constituent of the plaques of the complexus adhaerentes connecting certain lymphatic endothelial cells. Finally, we emphasize the occurrence of the desmosomal transmembrane glycoprotein, desmoglein Dsg2, out of the context of any junction as dispersed cell surface molecules in certain types of melanoma cells and melanocytes. This broadening of our knowledge on the diversity of AJ structures indicates that it may still be too premature to close the textbook chapters on cell-cell junctions.
Figures


References
-
- Cowin P, Franke WW, Grund C, Kapprell HP, Kartenbeck J. The desmosome-intermediate filament complex. In: Edelman GM, Thiery JP, editors. The Cell in Contact. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons; 1985. pp. 427–460.
-
- Godsel LM, Getsios S, Huen AC, Green KJ. The molecular composition and function of desmosomes. In: Behrens J, Nelson WJ, editors. Cell Adhesion. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer; 2004. pp. 137–193. - PubMed
-
- Garrod D, Chidgey M. Desmosome structure, composition and function. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2008;1778(3):572–587. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

