Archaea signal recognition particle shows the way
- PMID: 20672053
- PMCID: PMC2905702
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/485051
Archaea signal recognition particle shows the way
Abstract
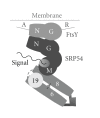
Archaea SRP is composed of an SRP RNA molecule and two bound proteins named SRP19 and SRP54. Regulated by the binding and hydrolysis of guanosine triphosphates, the RNA-bound SRP54 protein transiently associates not only with the hydrophobic signal sequence as it emerges from the ribosomal exit tunnel, but also interacts with the membrane-associated SRP receptor (FtsY). Comparative analyses of the archaea genomes and their SRP component sequences, combined with structural and biochemical data, support a prominent role of the SRP RNA in the assembly and function of the archaea SRP. The 5e motif, which in eukaryotes binds a 72 kilodalton protein, is preserved in most archaea SRP RNAs despite the lack of an archaea SRP72 homolog. The primary function of the 5e region may be to serve as a hinge, strategically positioned between the small and large SRP domain, allowing the elongated SRP to bind simultaneously to distant ribosomal sites. SRP19, required in eukaryotes for initiating SRP assembly, appears to play a subordinate role in the archaea SRP or may be defunct. The N-terminal A region and a novel C-terminal R region of the archaea SRP receptor (FtsY) are strikingly diverse or absent even among the members of a taxonomic subgroup.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure of the SRP19 RNA complex and implications for signal recognition particle assembly.Nature. 2002 Jun 13;417(6890):767-71. doi: 10.1038/nature00768. Epub 2002 Jun 5. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12050674
-
Archaeal SRP RNA and SRP19 facilitate the assembly of SRP54-FtsY targeting complex.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Aug 20;566:53-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.05.087. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 34116357
-
Unravelling the role of the A domain and N-terminal alpha-helices of FtsY in archaeal signal recognition particle.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;306(Pt 4):141645. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.141645. Epub 2025 Mar 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40032113
-
S-domain assembly of the signal recognition particle.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003 Feb;13(1):64-70. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00010-6. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 12581661 Review.
-
The archaeal signal recognition particle: steps toward membrane binding.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004 Feb;36(1):47-53. doi: 10.1023/b:jobb.0000019597.36170.5f. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004. PMID: 15168609 Review.
Cited by
-
Vestiges of the Bacterial Signal Recognition Particle-Based Protein Targeting in Mitochondria.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Jul 29;38(8):3170-3187. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab090. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33837778 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy: clinical features and pathogenesis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Dec;16(12):689-701. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00515-9. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 33093664 Review.
-
The Archaeal Signal Recognition Particle: Present Understanding and Future Perspective.Curr Microbiol. 2017 Feb;74(2):284-297. doi: 10.1007/s00284-016-1167-9. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Curr Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27900448 Review.
-
Piece by piece: Building a ribozyme.J Biol Chem. 2020 Feb 21;295(8):2313-2323. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV119.009929. Epub 2020 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31953324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the complete bacterial SRP Alu domain.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Oct 29;42(19):12284-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku883. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25270875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosenblad MA, Larsen N, Samuelsson T, Zwieb C. Kinship in the SRP RNA family. RNA Biology. 2009;6(5):508–516. - PubMed
-
- Stengel KF, Holdermann I, Cain P, Robinson C, Wild K, Sinning I. Structural basis for specific substrate recognition by the chloroplast signal recognition particle protein cpSRP43. Science. 2008;321(5886):253–256. - PubMed
-
- Moll RG. The archaeal signal recognition particle: steps toward membrane binding. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes. 2004;36(1):47–53. - PubMed
-
- Koch HG, Moser M, Müller M. Signal recognition particle-dependent protein targeting, universal to all kingdoms of life. Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology. 2003;146:55–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

