Nanodiamonds as Carriers for Address Delivery of Biologically Active Substances
- PMID: 20672079
- PMCID: PMC2894223
- DOI: 10.1007/s11671-010-9526-0
Nanodiamonds as Carriers for Address Delivery of Biologically Active Substances
Abstract
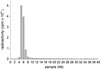
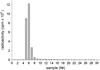
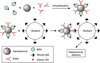
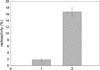
Surface of detonation nanodiamonds was functionalized for the covalent attachment of immunoglobulin, and simultaneously bovine serum albumin and Rabbit Anti-Mouse Antibody. The nanodiamond-IgG(I125) and RAM-nanodiamond-BSA(I125) complexes are stable in blood serum and the immobilized proteins retain their biological activity. It was shown that the RAM-nanodiamond-BSA(I125) complex is able to bind to the target antigen immobilized on the Sepharose 6B matrix through antibody-antigen interaction. The idea can be extended to use nanodiamonds as carriers for delivery of bioactive substances (i.e., drugs) to various targets in vivo.
Figures
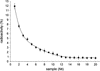
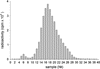
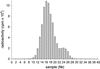
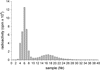



References
-
- Harrington KL, Lewanski CR, Stewart SW. Clin. 2000. p. 16. COI number [1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3htVGmuw%3D%3D] - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

