Maternally transferred anti-factor VIII IgG reduce the anti-factor VIII humoral immune response in factor VIII-deficient mice
- PMID: 20673239
- PMCID: PMC2999805
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03327.x
Maternally transferred anti-factor VIII IgG reduce the anti-factor VIII humoral immune response in factor VIII-deficient mice
Abstract
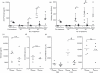
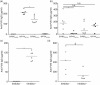
Replacement therapy with exogenous factor VIII (FVIII) to treat haemorrhages or used in prophylaxis induces inhibitory anti-FVIII immunoglobulin G (IgG) in some patients with haemophilia A. Therapeutic strategies to prevent the onset of the deleterious anti-FVIII immune response are still lacking. Maternal IgG is transferred to the offspring during fetal and neonatal life. While protecting the offspring from bacterial and viral infections, maternal IgG may alter the repertoires of T and B lymphocytes, and may impair vaccination in early infancy. Using haemophilic mice, we demonstrate that the transfer of maternal anti-FVIII IgG modulates the onset of anti-FVIII inhibitory IgG in early adulthood. The protective effect is reproduced upon reconstitution of naive mice with anti-FVIII IgG, suggesting that the reduced ability to mount an anti-FVIII immune response is the result of an interference between circulating anti-FVIII IgG and the administered FVIII rather than to a profound remodelling of lymphocyte repertoires occurring during the ontogeny of the immune system.
© 2010 The Authors. Immunology © 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
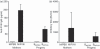
References
-
- Mariani G, Ghirardini A, Bellocco R. Immune tolerance in hemophilia: principal results from the international registry. Thromb Haemost. 1994;72:155–8. - PubMed
-
- Lacroix-Desmazes S, Navarrete AM, Andre S, Bayry J, Kaveri SV, Dasgupta S. Dynamics of factor VIII interactions determine its immunologic fate in hemophilia A. Blood. 2008;112:240–9. - PubMed
-
- Kurnik K, Bidlingmaier C, Engl W, Chehadeh H, Reipert B, Auerswald G. New early prophylaxis regimen that avoids immunological danger signals can reduce FVIII inhibitor development. Haemophilia. 2010;16:256–62. - PubMed
-
- Roopenian DC, Akilesh S. FcRn: the neonatal Fc receptor comes of age. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:715–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

