Simvastatin attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury in mice
- PMID: 20673352
- PMCID: PMC2945124
- DOI: 10.1186/cc9209
Simvastatin attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury in mice
Abstract
Introduction: Mechanical ventilation (MV) is a life saving intervention in acute respiratory failure without alternative. However, particularly in pre-injured lungs, even protective ventilation strategies may evoke ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI), which is characterized by pulmonary inflammation and vascular leakage. Adjuvant pharmacologic strategies in addition to lung protective ventilation to attenuate VILI are lacking. Simvastatin exhibited anti-inflammatory and endothelial barrier stabilizing properties in vitro and in vivo.
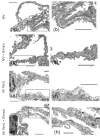
Methods: Mice were ventilated (12 ml/kg; six hours) and subjected to simvastatin (20 mg/kg) or sham treatment. Pulmonary microvascular leakage, oxygenation, pulmonary and systemic neutrophil and monocyte counts and cytokine release in lung and blood plasma were assessed. Further, lung tissue was analyzed by electron microscopy.
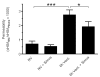
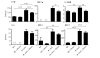
Results: Mechanical ventilation induced VILI, displayed by increased pulmonary microvascular leakage and endothelial injury, pulmonary recruitment of neutrophils and Gr-1high monocytes, and by liberation of inflammatory cytokines in the lungs. Further, VILI associated systemic inflammation characterized by blood leukocytosis and elevated plasma cytokines was observed. Simvastatin treatment limited pulmonary endothelial injury, attenuated pulmonary hyperpermeability, prevented the recruitment of leukocytes to the lung, reduced pulmonary cytokine levels and improved oxygenation in mechanically ventilated mice.
Conclusions: High-dose simvastatin attenuated VILI in mice by reducing MV-induced pulmonary inflammation and hyperpermeability.
Figures


Comment in
-
Protective role of statins against ventilator-induced lung injury.Crit Care. 2010;14(5):441. doi: 10.1186/cc9245. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Crit Care. 2010. PMID: 20860852 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Statins STAT for (over)ventilated patients?Crit Care. 2010;14(6):1014. doi: 10.1186/cc9318. Epub 2010 Dec 20. Crit Care. 2010. PMID: 21211068 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Esteban A, Anzueto A, Frutos F, Alia I, Brochard L, Stewart TE, Benito S, Epstein SK, Apezteguia C, Nightingale P, Arroliga AC, Tobin MJ. Characteristics and outcomes in adult patients receiving mechanical ventilation: a 28-day international study. JAMA. 2002;287:345–355. doi: 10.1001/jama.287.3.345. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

