[The sonodynamic effects of Chlorin e6 on the proliferation of human lung adenocarcinoma cell SPCA-1]
- PMID: 20673516
- PMCID: PMC6000541
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2010.03.03
[The sonodynamic effects of Chlorin e6 on the proliferation of human lung adenocarcinoma cell SPCA-1]
Abstract
Background and objective: Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) is a promising new approach for cancer therapy. The purpose of this study is to detect the effects of SDT on the cell proliferation of human lung adenocarcinoma cell SPCA-1, using Chlorin e6 as a sonosensitizing agent activated by ultrasound.
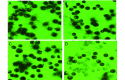
Methods: SPCA-1 and normal peripheral mononuclear cell (PMNC) were treated with ultrasound or Chlorin e6 alone and combined. Cell proliferation was determined by MTT assay, and cell morphology was studied by inverted microscope after 6 h treated.
Results: 1.0 MHz ultrasound (1.0 W/ cm(2)-2.0 W/cm2 x 60 s) and Chlorin e6 (0.4 mg/mL-3.2 mg/mL) inhibited the cell proliferation of both SPCA-1 and PMNC cells in a intensity- and a dose-dependent manner respectively. Compared with the ultrasound (1.0 W/cm2 x 60 s) or Chlorin e6 (0.05 mg/mL-0.2 mg/mL) alone, the inhibitory effect on the cell proliferation was remarkably increased by the combination of ultrasound and chlorin e6 in SPCA-1 cells (P < 0.05), but no same effect was observed in PMNC cells (P > 0.05). Compared with the ultrasound (1.0 W/cm2 x 60 s) or chlorin e6 (0.2 mg/mL) alone, the combination treatment of ultrasound with Chlorin e6 induced more necrotic cells in SPCA-1 cells (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: There was a significant selectively inhibitory effect of sonodynamic effect with Chlorin e6 on the SPCA-1 cell growth. Chlorin e6 may be a promising sonosensitizing agent for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.
背景与目的: 声动力治疗(sonodynamic therapy, SDT)是通过超声波激活肿瘤细胞内聚集的声敏剂来治疗肿瘤的一种新方法。本实验用二氢卟吩e6(Chlorin e6)为声敏剂,通过超声波激活,研究其对人肺腺癌细胞SPCA-1生长的作用。
方法: 超声与Chlorin e6单独及联合处理SPCA-1细胞和正常人外周血单核细胞(normal peripheral mononuclear cell, PMNC),6 h后四甲基偶氮唑盐(3-[4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2, 5-diphenyl -tetrazolium bromide, MTT)显色分光光度法测细胞增殖,倒置显微镜观察细胞形态。
结果: 1.0 MHz频率超声强度1.0 W/cm2-2.0 W/cm2作用60 s呈强度依赖性抑制SPCA-1和PMNC细胞生长。Chlorin e6(0.4 mg/mL-3.2 mg/mL)浓度依赖性地抑制SPCA-1和PMNC细胞生长。与单纯超声(1.0 W/cm2×60 s×1.0 MHz)和Chlorin e6(0.05 mg/mL-0.2 mg/mL)相比,超声联合Chlorin e6对SPCA-1细胞生长抑制作用明显增强(P < 0.05),对PMNC细胞抑制作用无明显变化(P > 0.05)。细胞形态显示,与单纯超声(1.0 W/cm2×60 s×1.0 MHz)和Chlorin e6(0.2 mg/mL)相比,超声联合Chlorin e6组SPCA-1细胞死亡率明显增多(P < 0.05)。
结论: 超声联合Chlorin e6声动力可特异性抑制人肺腺癌SPCA-1细胞生长,Chlorin e6有望成为一个用于声动力治疗非小细胞肺癌的新型声敏剂。
Figures
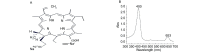



Similar articles
-
The tumor affinity of chlorin e6 and its sonodynamic effects on non-small cell lung cancer.Ultrason Sonochem. 2013 Mar;20(2):667-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2012.09.008. Epub 2012 Oct 2. Ultrason Sonochem. 2013. PMID: 23073382
-
[Adriamycin enhances the sonodynamic effect of chlorin e6 against the proliferation of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells in vitro].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2010 Oct;30(10):2291-4. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 20965828 Chinese.
-
Iron oxide nanoparticles as nanocarriers to improve chlorin e6-based sonosensitivity in sonodynamic therapy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Dec 10;12:4207-4216. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S184679. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30573951 Free PMC article.
-
Talaporfin: LS 11, LS11, ME 2906, mono-L-aspartyl chlorin e6, NP e6, NPE 6, taporfin sodium.Drugs R D. 2003;4(1):69-71. Drugs R D. 2003. Corrected and republished in: Drugs R D. 2003;4(2):135-7. PMID: 12568643 Corrected and republished. Review. No abstract available.
-
Sonodynamic therapy of cancer using novel sonosensitizers.Anticancer Res. 2007 Nov-Dec;27(6A):3673-7. Anticancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17970027 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Different Ultrasonic Parameters and Treatment Conditions to Optimize In Vitro Sonodynamic Therapeutic Effects in Cancer Cells.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Mar;82(1):303-314. doi: 10.1007/s12013-023-01189-2. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 37831307
References
-
- Yumita N, Okuyama N, Sasaki K, et al. Sonodynamic therapy on chemically induced mammary tumor: pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and sonodynamically induced antitumor effect of gallium-porphyrin complex ATX-70. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2007;60(6):891–897. doi: 10.1007/s00280-007-0436-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

