Properties of a general PK/PD model of antibody-ligand interactions for therapeutic antibodies that bind to soluble endogenous targets
- PMID: 20676036
- PMCID: PMC2958579
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.2.5.12833
Properties of a general PK/PD model of antibody-ligand interactions for therapeutic antibodies that bind to soluble endogenous targets
Abstract
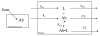
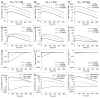
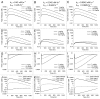
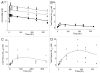
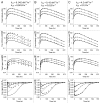
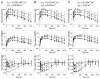
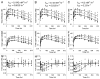
Antibodies that target endogenous soluble ligands are an important class of biotherapeutic agents. While much focus has been placed on characterization of antibody pharmacokinetics, less emphasis has been given to characterization of antibody effects on their soluble targets. We describe here the properties of a generalized mechanism-based PK/PD model used to characterize the in vivo interaction of an antibody and an endogenous soluble ligand. The assumptions and properties of the model are explored, and situations are described when deviations from the basic assumptions may be necessary. This model is most useful for in vivo situations where both antibody and ligand levels are available following drug administration. For a given antibody exposure, the extent and duration of suppression of free ligand is impacted by the apparent affinity of the interaction, as well as by the rate of ligand turnover. The applicability of the general equilibrium model of in vivo antibody-ligand interaction is demonstrated with an anti-Aß antibody.
Figures
References
-
- Wang W, Wang EQ, Balthasar JP. Monoclonal antibody pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008;84:548–558. - PubMed
-
- Benincosa LJ, Chow FS, Tobia LP, Kwok DC, Davis CB, Jusko WJ. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a humanized monoclonal antibody to factor IX in cynomolgus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;292:810–816. - PubMed
-
- Chow FS, Benincosa LJ, Sheth SB, Wilson D, Davis CB, Minthorn EA, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of humanized anti-factor IX antibody (SB 249417) in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002;71:235–245. - PubMed
-
- Jit M, Henderson B, Stevens M, Seymour RM. TNF-alpha neutralization in cytokine-driven diseases: a mathematical model to account for therapeutic success in rheumatoid arthritis but therapeutic failure in systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2005;44:323–331. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
