Consistency of predictive signature genes and classifiers generated using different microarray platforms
- PMID: 20676064
- PMCID: PMC2920073
- DOI: 10.1038/tpj.2010.34
Consistency of predictive signature genes and classifiers generated using different microarray platforms
Abstract
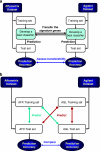
Microarray-based classifiers and associated signature genes generated from various platforms are abundantly reported in the literature; however, the utility of the classifiers and signature genes in cross-platform prediction applications remains largely uncertain. As part of the MicroArray Quality Control Phase II (MAQC-II) project, we show in this study 80-90% cross-platform prediction consistency using a large toxicogenomics data set by illustrating that: (1) the signature genes of a classifier generated from one platform can be directly applied to another platform to develop a predictive classifier; (2) a classifier developed using data generated from one platform can accurately predict samples that were profiled using a different platform. The results suggest the potential utility of using published signature genes in cross-platform applications and the possible adoption of the published classifiers for a variety of applications. The study reveals an opportunity for possible translation of biomarkers identified using microarrays to clinically validated non-array gene expression assays.
Figures




Comment in
-
Consistency of predictive signature genes and classifiers.Pharmacogenomics. 2011 Apr;12(4):461-3. doi: 10.2217/pgs.11.26. Pharmacogenomics. 2011. PMID: 21521018 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW, Brown PO. Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science. 1995;270:467–470. - PubMed
-
- van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van't Veer LJ, Dai H, Hart AA, Voskuil DW, et al. A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1999–2009. - PubMed
-
- Bammler T, Beyer RP, Bhattacharya S, Boorman GA, Boyles A, Bradford BU, et al. Standardizing global gene expression analysis between laboratories and across platforms. Nat Methods. 2005;2:351–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

