The aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacts with c-Maf to promote the differentiation of type 1 regulatory T cells induced by IL-27
- PMID: 20676095
- PMCID: PMC2940320
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1912
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacts with c-Maf to promote the differentiation of type 1 regulatory T cells induced by IL-27
Abstract
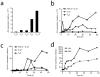
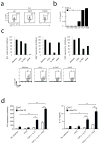
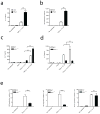
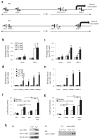
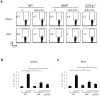
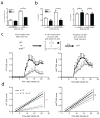
Type 1 regulatory T cells (Tr1 cells ) that produce interleukin 10 (IL-10) are instrumental in the prevention of tissue inflammation, autoimmunity and graft-versus-host disease. The transcription factor c-Maf is essential for the induction of IL-10 by Tr1 cells, but the molecular mechanisms that lead to the development of these cells remain unclear. Here we show that the ligand-activated transcription factor aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), which was induced by IL-27, acted in synergy with c-Maf to promote the development of Tr1 cells. After T cell activation under Tr1-skewing conditions, the AhR bound to c-Maf and promoted transactivation of the Il10 and Il21 promoters, which resulted in the generation of Tr1 cells and the amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Manipulating AhR signaling could therefore be beneficial in the resolution of excessive inflammatory responses.
Figures
Comment in
-
A toxin-sensitive receptor able to reduce immunopathology.Nat Immunol. 2010 Sep;11(9):779-81. doi: 10.1038/ni0910-779. Nat Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20720583 No abstract available.
-
Collaborative control of induced regulators.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 Sep;10(9):620. doi: 10.1038/nri2839. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21080598 No abstract available.
References
-
- Roncarolo MG, et al. Interleukin-10-secreting type 1 regulatory T cells in rodents and humans. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:28–50. - PubMed
-
- Pflanz S, et al. IL-27, a heterodimeric cytokine composed of EBI3 and p28 protein, induces proliferation of naive CD4(+) T cells. Immunity. 2002;16:779–790. - PubMed
-
- Villarino A, et al. The IL-27R (WSX-1) is required to suppress T cell hyperactivity during infection. Immunity. 2003;19:645–655. - PubMed
-
- Batten M, et al. Interleukin 27 limits autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing the development of interleukin 17-producing T cells. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:929–936. - PubMed
-
- Awasthi A, et al. A dominant function for interleukin 27 in generating interleukin 10-producing anti-inflammatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:1380–1389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AI075285/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI435801/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI093903/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI093903/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RG4111A1/RG/CSR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AI075285/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1K99AI075285/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01-ES11624/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES011624/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- NS38037/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01NS038037/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI039671/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01AI039671/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS038037/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

