Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors as promising cancer therapeutics
- PMID: 20676117
- PMCID: PMC4002295
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.103
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors as promising cancer therapeutics
Abstract
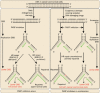
The year of 2005 was a watershed in the history of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors due to the important findings of selective killing in BRCA-deficient cancers by PARP inhibition. The findings made PARP inhibition one of the most promising new therapeutic approaches to cancers, especially to those with specific defects. With AZD2281 and BSI-201 entering phase III clinical trials, the final application of PARP inhibitors in clinic would come true soon. This current paper will review the major advances in targeting PARP for cancer therapy and discuss the existing questions, the answers to which may influence the future of PARP inhibitors as cancer therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Bryant HE, Schultz N, Thomas HD, Parker KM, Flower D, Lopez E, et al. Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature. 2005;434:913–7. - PubMed
-
- Farmer H, McCabe N, Lord CJ, Tutt AN, Johnson DA, Richardson TB, et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature. 2005;434:917–21. - PubMed
-
- Schreiber V, Dantzer F, Ame JC, de Murcia G. Poly(ADP-ribose): novel functions for an old molecule. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:517–28. - PubMed
-
- Ferraris DV. Evolution of Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase-1 (PARP-1) Inhibitors. From Concept to Clinic. J Med Chem. 2010;53:4561–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

