Keloids: pathogenesis, clinical features, and management
- PMID: 20676312
- PMCID: PMC2884925
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0029-1224797
Keloids: pathogenesis, clinical features, and management
Abstract
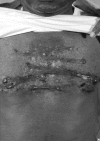
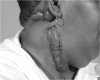
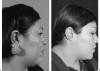
Cutaneous wound healing is a complex response to skin injury. Deregulation of this process can lead to excessive scar formation, as seen in keloids. Keloids are common skin lesions that are difficult to treat and are associated with high recurrence rates despite the large number of available treatment options. With increased knowledge of the disease process and further scientific advancements, future approaches will hopefully improve keloid treatment. In this article, we review the epidemiology, genetic basis, etiology, clinical features, pathogenesis, and management of keloids.
Keywords: Keloid; hypertrophic scar; treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Bayat A, Bock O, Mrowietz U, Ollier W E, Ferguson M W. Genetic susceptibility to keloid disease and hypertrophic scarring: transforming growth factor beta1 common polymorphisms and plasma levels. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111:535–543. discussion 544–546. - PubMed
-
- Brissett A E, Sherris D A. Scar contractures, hypertrophic scars, and keloids. Facial Plast Surg. 2001;17:263–272. - PubMed
-
- Marneros A G, Krieg T. Keloids—clinical diagnosis, pathogenesis, and treatment options. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2004;2:905–913. - PubMed
-
- Messadi D V, Le A, Berg S, Huang G, Zhuang W, Bertolami C N. Effect of TGF-beta 1 on PDGF receptors expression in human scar fibroblasts. Front Biosci. 1998;3:a16–a22. - PubMed
-
- Sayah D N, Soo C, Shaw W W, et al. Downregulation of apoptosis-related genes in keloid tissues. J Surg Res. 1999;87:209–216. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

