The dynamic stress-induced "O-GlcNAc-ome" highlights functions for O-GlcNAc in regulating DNA damage/repair and other cellular pathways
- PMID: 20676906
- PMCID: PMC3329784
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-010-0695-z
The dynamic stress-induced "O-GlcNAc-ome" highlights functions for O-GlcNAc in regulating DNA damage/repair and other cellular pathways
Abstract
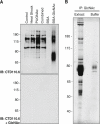
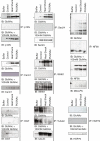
The modification of nuclear, mitochondrial, and cytoplasmic proteins by O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) is a dynamic and essential post-translational modification of metazoans. Numerous forms of cellular injury lead to elevated levels of O-GlcNAc in both in vivo and in vitro models, and elevation of O-GlcNAc levels before, or immediately after, the induction of cellular injury is protective in models of heat stress, oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, hypoxia, ischemia reperfusion injury, and trauma hemorrhage. Together, these data suggest that O-GlcNAc is a regulator of the cellular stress response. However, the molecular mechanism(s) by which O-GlcNAc regulates protein function leading to enhanced cell survival have not been identified. In order to determine how O-GlcNAc modulates stress tolerance in these models we have used stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture to determine the identity of proteins that undergo O-GlcNAcylation in response to heat shock. Numerous proteins with diverse functions were identified, including NF-90, RuvB-like 1 (Tip49α), RuvB-like 2 (Tip49β), and several COPII vesicle transport proteins. Many of these proteins bind double-stranded DNA-dependent protein kinase (PK), or double-stranded DNA breaks, suggesting a role for O-GlcNAc in regulating DNA damage signaling or repair. Supporting this hypothesis, we have shown that DNA-PK is O-GlcNAc modified in response to numerous forms of cellular stress.
Figures



References
-
- Amanchy R, Kalume DE, Pandey A. Stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) for studying dynamics of protein abundance and posttranslational modifications. Sci STKE 2005. 2005:12. - PubMed
-
- Amodio G, Renna M, Paladino S, Venturi C, Tacchetti C, Moltedo O, Franceschelli S, Mallardo M, Bonatti S, Remondelli P. Endoplasmic reticulum stress reduces the export from the ER and alters the architecture of post-ER compartments. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;41:2511–2521. - PubMed
-
- Bauer I, Graessle S, Loidl P, Hohenstein K, Brosch G. Novel insights into the functional role of three protein arginine methyltransferases in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol. 2010 - PubMed
-
- Bauer I, Graessle S, Loidl P, Hohenstein K, Brosch G. Novel insights into the functional role of three protein arginine methyltransferases in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol. 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

