Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 surveillance for severe illness and response, New York, New York, USA, April-July 2009
- PMID: 20678320
- PMCID: PMC3298321
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1608.091847
Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 surveillance for severe illness and response, New York, New York, USA, April-July 2009
Abstract
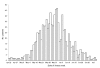
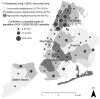
On April 23, 2009, the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene (DOHMH) was notified of a school outbreak of respiratory illness; 2 days later the infection was identified as pandemic (H1N1) 2009. This was the first major outbreak of the illness in the United States. To guide decisions on the public health response, the DOHMH used active hospital-based surveillance and then enhanced passive reporting to collect data on demographics, risk conditions, and clinical severity. This surveillance identified 996 hospitalized patients with confirmed or probable pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus infection from April 24 to July 7; fifty percent lived in high-poverty neighborhoods. Nearly half were <18 years of age. Surveillance data were critical in guiding the DOHMH response. The DOHMH experience during this outbreak illustrates the need for the capacity to rapidly expand and modify surveillance to adapt to changing conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus infections in a school—New York City, April 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:470–2. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: swine influenza A (H1N1) infections—California and Texas, April 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:435–7. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Swine influenza A (H1N1) infection in two children—Southern California, March–April 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:400–2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
