The eccentric cleavage product of β-carotene, β-apo-13-carotenone, functions as an antagonist of RXRα
- PMID: 20678466
- PMCID: PMC3517194
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.07.025
The eccentric cleavage product of β-carotene, β-apo-13-carotenone, functions as an antagonist of RXRα
Abstract
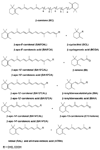
In this study, we investigated the effects of eccentric cleavage products of β-carotene, i.e. β-apocarotenoids (BACs), on retinoid X receptor alpha (RXRα) signaling. Transactivation assays were performed to test whether BACs activate or antagonize RXRα. Reporter gene constructs (RXRE-Luc, pRL-tk) and RXRα were transfected into Cos-1 cells and used to perform these assays. None of the BACs tested activated RXRα. Among the compounds tested, β-apo-13-carotenone was found to antagonize the activation of RXRα by 9-cis-retinoic acid and was effective at concentrations as low as 1 nM. Molecular modeling studies revealed that β-apo-13-carotenone makes molecular interactions like an antagonist of RXRα. The results suggest a possible function of BACs on RXRα signaling.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

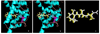

Similar articles
-
β-Apo-13-carotenone regulates retinoid X receptor transcriptional activity through tetramerization of the receptor.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 28;289(48):33118-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.610501. Epub 2014 Oct 16. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25324544 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally occurring eccentric cleavage products of provitamin A β-carotene function as antagonists of retinoic acid receptors.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 4;287(19):15886-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.325142. Epub 2012 Mar 14. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22418437 Free PMC article.
-
The formation, occurrence, and function of β-apocarotenoids: β-carotene metabolites that may modulate nuclear receptor signaling.Am J Clin Nutr. 2012 Nov;96(5):1189S-92S. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.034843. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012. PMID: 23053561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carotenoids, β-Apocarotenoids, and Retinoids: The Long and the Short of It.Nutrients. 2022 Mar 28;14(7):1411. doi: 10.3390/nu14071411. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35406024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transactivation of the human retinoid X receptor by organotins: use of site-directed mutagenesis to identify critical amino acid residues for organotin-induced transactivation.Metallomics. 2015 Jul;7(7):1180-8. doi: 10.1039/c5mt00086f. Metallomics. 2015. PMID: 25985376
Cited by
-
β-Apo-10'-carotenoids Modulate Placental Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein Expression and Function to Optimize Transport of Intact β-Carotene to the Embryo.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 26;291(35):18525-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.738336. Epub 2016 Jul 8. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27402843 Free PMC article.
-
β-Carotene Oxygenase 2 Genotype Modulates the Impact of Dietary Lycopene on Gene Expression during Early TRAMP Prostate Carcinogenesis.J Nutr. 2022 Apr 1;152(4):950-960. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxab445. J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34964896 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate specificity of purified recombinant human β-carotene 15,15'-oxygenase (BCO1).J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 27;288(52):37094-103. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.507160. Epub 2013 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24187135 Free PMC article.
-
Two carotenoid oxygenases contribute to mammalian provitamin A metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 22;288(47):34081-34096. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.501049. Epub 2013 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24106281 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between β-carotene and lipoprotein metabolism at the maternal-fetal barrier.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020 Nov;1865(11):158591. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.158591. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020. PMID: 31863969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Römer S, Fraser PD. Recent advances in carotenoid biosynthesis, regulation, and manipulation. Planta. 2005;221:1533–1535. - PubMed
-
- Spurgeon SL, Porter JW. Biosynthesis of carotenoids, Biosynthesis of lsoprenoid Compounds. vol. 2. New York: Wiley & Sons; 1983. pp. 1–122.
-
- Olson JA, Krinsky NI. Introduction: the colorful, fascinating world of the carotenoids: important physiologic modulators. FASEB J. 1995;9:1547–1550. - PubMed
-
- Parker RS. Absorption, metabolism, and transport of carotenoids. FASEB J. 1996;10:542–551. - PubMed
-
- Wirtz GM, Bornemann C, Giger A, Muller RK, Schneider H, Schlotterbeck G, Schiefer G, Woggon WD. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2001;84:2315–3201.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

