Cyclothiazide induces seizure behavior in freely moving rats
- PMID: 20678492
- PMCID: PMC2947190
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.07.088
Cyclothiazide induces seizure behavior in freely moving rats
Abstract
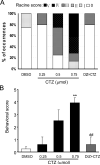
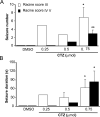
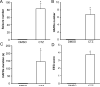
We have previously demonstrated that cyclothiazide (CTZ) is a potent convulsant drug inducing robust epileptiform activity in hippocampal neurons both in vitro and in vivo. Here we further establish an animal model for CTZ-induced behavioral seizures in freely moving rats. Microinjection of CTZ into the left ventricle dose-dependently induced robust seizure behaviors within 3h after administration. At a dose of 0.75 μmol, CTZ induced Racine score IV-V seizure behaviors in 71% (n=14) of the rats were tested. In addition, CTZ also induced epileptiform EEG activity accompanying behavioral seizures. The convulsant action of CTZ on both behavior and EEG was blocked by pretreatment with clinical anticonvulsant drug diazepam (n=5). In conclusion, our results demonstrate that CTZ is capable of inducing behavioral seizures in intact animals. Since CTZ acts on both GABAergic and glutamatergic systems, this new animal epilepsy model will be useful for anticonvulsant drug testing and general epilepsy research.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
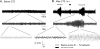

Similar articles
-
BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway mediates the induction of epileptiform activity induced by a convulsant drug cyclothiazide.Neuropharmacology. 2009 Jul;57(1):49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.04.007. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Neuropharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19393251 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors inhibits cyclothiazide-induced epileptiform activity in hippocampal CA1 neurons.Neurosci Bull. 2014 Oct;30(5):866-76. doi: 10.1007/s12264-014-1466-8. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Neurosci Bull. 2014. PMID: 25260800 Free PMC article.
-
Epileptiform response of CA1 neurones to convulsant stimulation by cyclothiazide, kainic acid and pentylenetetrazol in anaesthetized rats.Seizure. 2011 May;20(4):312-9. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2010.12.016. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Seizure. 2011. PMID: 21269843
-
Downregulated GABA and BDNF-TrkB pathway in chronic cyclothiazide seizure model.Neural Plast. 2014;2014:310146. doi: 10.1155/2014/310146. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Neural Plast. 2014. PMID: 24757570 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclothiazide induces robust epileptiform activity in rat hippocampal neurons both in vitro and in vivo.J Physiol. 2006 Mar 15;571(Pt 3):605-18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.103812. Epub 2006 Jan 19. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16423850 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Proconvulsive effect of hydrochlorothiazide in an in vitro rat seizure model.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014 Nov;17(11):860-6. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25691927 Free PMC article.
-
KCC2 downregulation facilitates epileptic seizures.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 13;7(1):156. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00196-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28279020 Free PMC article.
-
M-Calpain Activation Facilitates Seizure Induced KCC2 Down Regulation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Aug 21;11:287. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00287. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30186110 Free PMC article.
-
X-linked neonatal-onset epileptic encephalopathy associated with a gain-of-function variant p.R660T in GRIA3.PLoS Genet. 2021 Jun 23;17(6):e1009608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009608. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34161333 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal injury and death following focal mild brain injury: The role of network excitability and seizure.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Jan;23(1):63-70. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2019.37558.8932. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32405349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai ZT, Zhao R, Zhang XY, Chen J, Liu T, Ji YH. The epileptic seizures induced by BmK I, a modulator of sodium channels. Exp Neurol. 2006;197:167–176. - PubMed
-
- Bellingham MC, Walmsley B. A novel presynaptic inhibitory mechanism underlies paired pulse depression at a fast central synapse. Neuron. 1999;23:159–70. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y, Lagowska J. Epileptogenic Action of Intra-amygdaloid Injection of Kainic Acid. Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires Des Seances De L Academie Des Sciences Serie D. 1978;287:813–816. - PubMed
-
- Browne TR, Holmes GL. Epilepsy. Reply. New Engl J Med. 2001;345:468–469. - PubMed

