High-resolution, high-contrast ultrasound imaging using a prototype dual-frequency transducer: in vitro and in vivo studies
- PMID: 20679006
- PMCID: PMC2945691
- DOI: 10.1109/TUFFC.2010.1615
High-resolution, high-contrast ultrasound imaging using a prototype dual-frequency transducer: in vitro and in vivo studies
Abstract
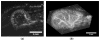
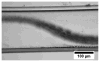
With recent advances in animal models of disease, there has been great interest in capabilities for highresolution contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging. Microbubble contrast agents are unique in that they scatter broadband ultrasound energy because of their nonlinear behavior. For optimal response, it is desirable to excite the microbubbles near their resonant frequency. To date, this has been challenging with high-frequency imaging systems because most contrast agents are resonant at frequencies in the order of several megahertz. Our team has developed a unique dual-frequency confocal transducer which enables low-frequency excitation of bubbles near their resonance with one element, and detection of their emitted high-frequency content with the second element. Using this imaging approach, we have attained an average 12.3 dB improvement in contrast-to-tissue ratios over fundamental mode imaging, with spatial resolution near that of the high-frequency element. Because this detection method does not rely on signal decorrelation, it is not susceptible to corruption by tissue motion. This probe demonstrates contrast imaging capability with significant tissue suppression, enabling high-resolution contrast-enhanced images of microvascular blood flow. Additionally, this probe can readily produce radiation force on flowing contrast agents, which may be beneficial for targeted imaging or therapy.
Figures

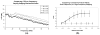


References
-
- Turnbull DH, Ramsay JA, Shivji GS, Bloomfield TS, From L, Sauder DN, Foster FS. Ultrasound backscatter microscope analysis of mouse melanoma progression. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1996;22(7):845–853. - PubMed
-
- Chomas JE, Pollard RE, Sadlowski AR, Griffey SM, Wisner ER, Ferrara KW. Contrast-enhanced US of microcirculation of superficially implanted tumors in rats. Radiology. 2003 Nov;229(2):439–446. - PubMed
-
- Elie N, Kaliski A, Péronneau P, Opolon P, Roche A, Lassau N. Methodology for quantifying interactions between perfusion evaluated by DCE-US and hypoxia throughout tumor growth. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2007 Apr;33(4):549–560. - PubMed
-
- Foster FS, Burns PN, Simpson DH, Wilson SR, Christopher DA, Goertz DE. Ultrasound for the visualization and quantification of tumor microcirculation. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2000;19(1–2):131–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

