A tumor-suppressing mechanism in Drosophila involving cell competition and the Hippo pathway
- PMID: 20679206
- PMCID: PMC2930466
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1009376107
A tumor-suppressing mechanism in Drosophila involving cell competition and the Hippo pathway
Abstract
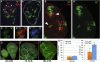
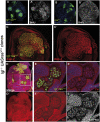
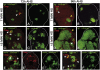
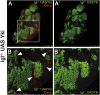
Mutant larvae for the Drosophila gene lethal giant larva (lgl) develop neoplastic tumors in imaginal discs. However, lgl mutant clones do not form tumors when surrounded by wild-type tissue, suggesting the existence of a tumor-suppressing mechanism. We have investigated the tumorigenic potential of lgl mutant cells by generating wing compartments that are entirely mutant for lgl and also inducing clones of various genetic combinations of lgl(-) cells. We find that lgl(-) compartments can grow indefinitely but lgl(-) clones are eliminated by cell competition. lgl mutant cells may form tumors if they acquire constitutive activity of the Ras pathway (lgl(-) UAS-ras(V12)), which confers proliferation advantage through inhibition of the Hippo pathway. Yet, the majority of lgl(-) UAS-ras(V12) clones are eliminated in spite of their high proliferation rate. The formation of a tumor requires in addition the formation of a microenvironment that allows mutant cells to evade cell competition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Tumorigenesis: To the death!Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Sep;10(9):598. doi: 10.1038/nrc2924. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20803809 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bilder D. Epithelial polarity and proliferation control: Links from the Drosophila neoplastic tumor suppressors. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1909–1925. - PubMed
-
- Hariharan IK, Bilder D. Regulation of imaginal disc growth by tumor-suppressor genes in Drosophila. Annu Rev Genet. 2006;40:335–361. - PubMed
-
- Knoblich JA. Mechanisms of asymmetric stem cell division. Cell. 2008;132:583–597. - PubMed
-
- Humbert PO, et al. Control of tumourigenesis by the Scribble/Dlg/Lgl polarity module. Oncogene. 2008;27:6888–6907. - PubMed
-
- Kuphal S, et al. Expression of Hugl-1 is strongly reduced in malignant melanoma. Oncogene. 2006;25:103–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

