Nucleobindin 1 is a calcium-regulated guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor of G{alpha}i1
- PMID: 20679342
- PMCID: PMC2951237
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.148429
Nucleobindin 1 is a calcium-regulated guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor of G{alpha}i1
Abstract
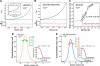
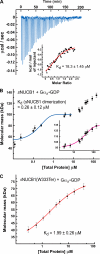
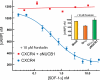
Nucleobindin 1 (NUCB1) is a widely expressed multidomain calcium-binding protein whose precise physiological and biochemical functions are not well understood. We engineered and heterologously expressed a soluble form of NUCB1 (sNUCB1) and characterized its biophysical and biochemical properties. We show that sNUCB1 exists as a dimer in solution and that each monomer binds two divalent calcium cations. Calcium binding causes conformational changes in sNUCB1 as judged by circular dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy experiments. Earlier reports suggested that NUCB1 might interact with heterotrimeric G protein α subunits. We show that dimeric calcium-free sNUCB1 binds to expressed Gα(i1) and that calcium binding inhibits the interaction. The binding of sNUCB1 to Gα(i1) inhibits its basal rate of GDP release and slows its rate and extent of GTPγS uptake. Additionally, our tissue culture experiments show that sNUCB1 prevents receptor-mediated Gα(i)-dependent inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. Thus, we conclude that sNUCB1 is a calcium-dependent guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI) for Gα(i1). To our knowledge, sNUCB1 is the first example of a calcium-dependent GDI for heterotrimeric G proteins. We also show that the mechanism of GDI activity of sNUCB1 is unique and does not arise from the consensus GoLoco motif found in RGS proteins. We propose that cytoplasmic NUCB1 might function to regulate heterotrimeric G protein trafficking and G protein-coupled receptor-mediated signal transduction pathways.
Figures



References
-
- Oldham W. M., Hamm H. E. (2008) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 60–71 - PubMed
-
- Sakmar T. P., Menon S. T., Marin E. P., Awad E. S. (2002) Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 31, 443–484 - PubMed
-
- Gilman A. G. (1987) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 56, 615–649 - PubMed
-
- Pierce K. L., Premont R. T., Lefkowitz R. J. (2002) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 639–650 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

