The EspF effector, a bacterial pathogen's Swiss army knife
- PMID: 20679436
- PMCID: PMC2976335
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00635-10
The EspF effector, a bacterial pathogen's Swiss army knife
Abstract
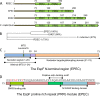
Central to the pathogenesis of many bacterial pathogens is the ability to deliver effector proteins directly into the cells of their eukaryotic host. EspF is one of many effector proteins exclusive to the attaching and effacing pathogen family that includes enteropathogenic (EPEC) and enterohemorrhagic (EHEC) Escherichia coli. Work in recent years has revealed EspF to be one of the most multifunctional effector proteins known, with defined roles in several host cellular processes, including disruption of the epithelial barrier, antiphagocytosis, microvillus effacement, host membrane remodelling, modulation of the cytoskeleton, targeting and disruption of the nucleolus, intermediate filament disruption, cell invasion, mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, and inhibition of several important epithelial transporters. Surprisingly, despite this high number of functions, EspF is a relatively small effector protein, and recent work has begun to decipher the molecular events that underlie its multifunctionality. This review focuses on the activities of EspF within the host cell and discusses recent findings and molecular insights relating to the virulence functions of this fascinating bacterial effector.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The enteropathogenic E. coli effector EspF targets and disrupts the nucleolus by a process regulated by mitochondrial dysfunction.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Jun 24;6(6):e1000961. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000961. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20585567 Free PMC article.
-
EspZ of enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli regulates type III secretion system protein translocation.mBio. 2012 Oct 2;3(5):e00317-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00317-12. Print 2012. mBio. 2012. PMID: 23033475 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminal domain of EspF induces host cell apoptosis after infection with enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055164. Epub 2013 Jan 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23372831 Free PMC article.
-
Enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli: even more subversive elements.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Jun;80(6):1420-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07661.x. Epub 2011 May 5. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21488979 Review.
-
Modulation of the Inflammasome Signaling Pathway by Enteropathogenic and Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Aug 26;6:89. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00089. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27617233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Guanylate cyclase C limits systemic dissemination of a murine enteric pathogen.BMC Gastroenterol. 2013 Sep 2;13:135. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-13-135. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24004613 Free PMC article.
-
An Escherichia coli Effector Protein EspF May Induce Host DNA Damage via Interaction With SMC1.Front Microbiol. 2021 May 26;12:682064. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.682064. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34122393 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the pathogenesis of enteropathogenic E. coli using an improved intestinal enterocyte model.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055284. Epub 2013 Jan 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383137 Free PMC article.
-
The EHEC-host interactome reveals novel targets for the translocated intimin receptor.Sci Rep. 2014 Dec 18;4:7531. doi: 10.1038/srep07531. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25519916 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolar c-Myc recruitment by a Vibrio T3SS effector promotes host cell proliferation and bacterial virulence.EMBO J. 2021 Jan 15;40(2):e105699. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105699. Epub 2020 Dec 21. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 33347626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alto, N. M., A. W. Weflen, M. J. Rardin, D. Yarar, C. S. Lazar, R. Tonikian, A. Koller, S. S. Taylor, C. Boone, S. S. Sidhu, S. L. Schmid, G. A. Hecht, and J. E. Dixon. 2007. The type III effector EspF coordinates membrane trafficking by the spatiotemporal activation of two eukaryotic signaling pathways. J. Cell Biol. 178:1265-1278. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boisvert, F. M., S. van Koningsbruggen, J. Navascues, and A. I. Lamond. 2007. The multifunctional nucleolus. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8:574-585. - PubMed
-
- Campellone, K. G., H. C. Cheng, D. Robbins, A. D. Siripala, E. J. McGhie, R. D. Hayward, M. D. Welch, M. K. Rosen, V. Koronakis, and J. M. Leong. 2008. Repetitive N-WASP-binding elements of the enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli effector EspF(U) synergistically activate actin assembly. PLoS Pathog. 4:e1000191. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campellone, K. G., D. Robbins, and J. M. Leong. 2004. EspFU is a translocated EHEC effector that interacts with Tir and N-WASP and promotes Nck-independent actin assembly. Dev. Cell 7:217-228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

