Identification of the TcpP-binding site in the toxT promoter of Vibrio cholerae and the role of ToxR in TcpP-mediated activation
- PMID: 20679441
- PMCID: PMC2950353
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00566-10
Identification of the TcpP-binding site in the toxT promoter of Vibrio cholerae and the role of ToxR in TcpP-mediated activation
Abstract
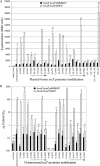
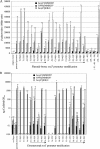
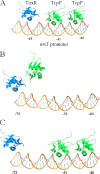
ToxR-dependent recruitment of TcpP to the toxT promoter facilitates toxT transcription in Vibrio cholerae, initiating a regulatory cascade that culminates in cholera toxin expression and secretion. Although TcpP usually requires ToxR to activate the toxT promoter, TcpP overexpression can circumvent the requirement for ToxR in this process. To define nucleotides critical for TcpP-dependent promoter recognition and activation, a series of toxT promoter derivatives with single-base-pair transversions spanning the TcpP-binding site were generated and used as plasmid-borne toxT-lacZ fusions, as DNA mobility shift targets, and as allelic replacements of the chromosomal toxT promoter. When present in ΔtoxR V. cholerae overexpressing TcpP, several transversions affecting nucleotides within two direct repeats present in the TcpP-binding region (TGTAA-N(6)-TGTAA) caused defects in TcpP-dependent toxT-lacZ fusion activation and toxin production. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays demonstrated that these same transversions reduced the affinity of the toxT promoter for TcpP. The presence of ToxR suppressed transcription activation defects associated with most, but not all, transversions. Particularly, the central thymine nucleotide of both pentameric repeats was essential for efficient toxT activation, even in the presence of ToxR. These results suggest that the toxT promoter recognition function provided by ToxR can facilitate the interaction of TcpP with the toxT promoter but is insufficient for promoter activation when the TcpP-binding site has been severely compromised by mutation. Thus, the interaction of TcpP with nucleotides of the direct repeat sequences appears to be a prerequisite for toxT promoter activation.
Figures


References
-
- Blanco, A. G., M. Sola, F. X. Gomis-Ruth, and M. Coll. 2002. Tandem DNA recognition by PhoB, a two-component signal transduction transcriptional activator. Structure 10:701-713. - PubMed
-
- Higgins, D. E., and V. J. DiRita. 1994. Transcriptional control of toxT, a regulatory gene in the ToxR regulon of Vibrio cholerae. Mol. Microbiol. 14:17-29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

