The type I interferon signaling pathway is a target for glucocorticoid inhibition
- PMID: 20679482
- PMCID: PMC2950533
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00146-10
The type I interferon signaling pathway is a target for glucocorticoid inhibition
Abstract
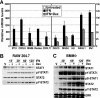
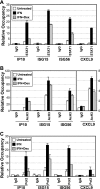
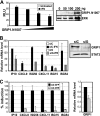
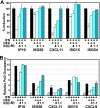
Type I interferon (IFN) is essential for host defenses against viruses; however, dysregulated IFN signaling is causally linked to autoimmunity, particularly systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmune disease treatments rely on glucocorticoids (GCs), which act via the GC receptor (GR) to repress proinflammatory cytokine gene transcription. Conversely, cytokine signaling through cognate Jak/STAT pathways is reportedly unaffected or even stimulated by GR. Unexpectedly, we found that GR dramatically inhibited IFN-stimulated gene (ISG) expression in macrophages. The target of inhibition, the heterotrimeric STAT1-STAT2-IRF9 (ISGF3) transcription complex, utilized the GR cofactor GRIP1/TIF2 as a coactivator. Consequently, GRIP1 knockdown, genetic ablation, or depletion by GC-activated GR attenuated ISGF3 promoter occupancy, preinitiation complex assembly, and ISG expression. Furthermore, this regulatory loop was restricted to cell types such as macrophages expressing the GRIP1 protein at extremely low levels, and pharmacological disruption of the GR-GRIP1 interaction or transient introduction of GRIP1 restored RNA polymerase recruitment to target ISGs and the subsequent IFN response. Thus, type I IFN is a cytokine uniquely controlled by GR at the levels of not only production but also signaling through antagonism with the ISGF3 effector function, revealing a novel facet of the immunosuppressive properties of GCs.
Figures



References
-
- Aittomaki, S., M. Pesu, B. Groner, O. A. Janne, J. J. Palvimo, and O. Silvennoinen. 2000. Cooperation among Stat1, glucocorticoid receptor, and PU.1 in transcriptional activation of the high-affinity Fc gamma receptor I in monocytes. J. Immunol. 164:5689-5697. - PubMed
-
- An, J., R. C. Ribeiro, P. Webb, J. A. Gustafsson, P. J. Kushner, J. D. Baxter, and D. C. Leitman. 1999. Estradiol repression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha transcription requires estrogen receptor activation function-2 and is enhanced by coactivators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96:15161-15166. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baechler, E. C., F. M. Batliwalla, G. Karypis, P. M. Gaffney, W. A. Ortmann, K. J. Espe, K. B. Shark, W. J. Grande, K. M. Hughes, V. Kapur, P. K. Gregersen, and T. W. Behrens. 2003. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100:2610-2615. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
