Distribution of small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoproteins (SIBLING) in the articular cartilage of the rat femoral head
- PMID: 20679519
- PMCID: PMC2958136
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.2010.956771
Distribution of small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoproteins (SIBLING) in the articular cartilage of the rat femoral head
Abstract
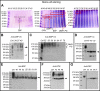
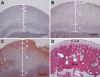
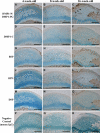
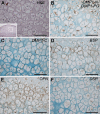
The small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoprotein (SIBLING) family is closely related to osteogenesis. Until recently, little was known about their existence in articular cartilage. In this study, we systematically evaluated the presence and distribution of four SIBLING family members in rat femoral head cartilage: dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1), bone sialoprotein (BSP), osteopontin (OPN), and dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP). First, non-collagenous proteins were extracted and then separated by ion-exchange chromatography. Next, the protein extracts eluted by chromatography were analyzed by Stains-all staining and Western immunoblotting. IHC was used to assess the distribution of these four SIBLING family members in the femoral head cartilage. Both approaches showed that all the four SIBLING family members are expressed in the femoral head cartilage. IHC showed that SIBLING members are distributed in various locations throughout the articular cartilage. The NH₂-terminal fragments of DMP1, BSP, and OPN are present in the cells and in the extracellular matrix, whereas the COOH-terminal fragment of DMP1 and the NH₂-terminal fragment of DSPP are primarily intracellularly localized in the chondrocytes. The presence of the SIBLING family members in the rat femoral head cartilage suggests that they may play important roles in chondrogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distribution of small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoproteins (SIBLING) in the condylar cartilage of rat mandible.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010 Mar;39(3):272-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2009.12.017. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010. PMID: 20097540 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of SIBLING proteins in the organic and inorganic phases of rat dentin and bone.Eur J Oral Sci. 2008 Apr;116(2):104-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.2008.00522.x. Eur J Oral Sci. 2008. PMID: 18353003 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications of sibling proteins and their roles in osteogenesis and dentinogenesis.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2004 Jun 4;15(3):126-36. doi: 10.1177/154411130401500302. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2004. PMID: 15187031 Review.
-
Distribution and expression of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein and bone sialoprotein show marked changes during rat femoral head development.Matrix Biol. 1995 Dec;14(9):773-81. doi: 10.1016/s0945-053x(05)80020-4. Matrix Biol. 1995. PMID: 8785592
-
[SIBLING proteins: molecular tools for tumor progression and angiogenesis].Med Sci (Paris). 2013 Nov;29(11):1018-25. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20132911019. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Med Sci (Paris). 2013. PMID: 24280506 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Immunohistochemical localization of the NH(2)-terminal and COOH-terminal fragments of dentin sialoprotein in mouse teeth.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Aug;349(2):605-14. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1418-4. Epub 2012 May 13. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 22581382 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of Fam20C in cells expressing type I collagen causes periodontal disease in mice.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 5;9(12):e114396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114396. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25479552 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylation of dentin matrix protein 1 is critical for fracture healing via promoting chondrogenesis.Front Med. 2019 Oct;13(5):575-589. doi: 10.1007/s11684-019-0693-9. Epub 2019 May 8. Front Med. 2019. PMID: 31065929
-
An in situ hybridization study of perlecan, DMP1, and MEPE in developing condylar cartilage of the fetal mouse mandible and limb bud cartilage.Eur J Histochem. 2015 Sep 25;59(3):2553. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2015.2553. Eur J Histochem. 2015. PMID: 26428891 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of DMP1 processing in osteogenesis, dentinogenesis and chondrogenesis.Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;194(2-4):199-204. doi: 10.1159/000324672. Epub 2011 May 9. Cells Tissues Organs. 2011. PMID: 21555863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attur MG, Dave MN, Stuchin S, Kowalski AJ, Steiner G, Abramson SB, Denhardt DT, et al. (2001) Osteopontin: an intrinsic inhibitor of inflammation in cartilage. Arthritis Rheum 44:578–584 - PubMed
-
- Baba O, Qin C, Brunn JC, Jones JE, Wygant JN, McIntyre BW, Butler WT (2004a) Detection of dentin sialoprotein in rat periodontium. Eur J Oral Sci 112:163–170 - PubMed
-
- Baba O, Qin C, Brunn JC, Wygant JN, Mcintyre BW, Butler WT (2004b) Colocalization of dentin matrix protein 1 and dentin sialoprotein at late stages of rat molar development. Matrix Biol 23:371–379 - PubMed
-
- Boskey AL, Maresca M, Ullrich W, Doty SB, Butler WT, Prince CW (1993) Osteopontin–hydroxyapatite interactions in vitro: inhibition of hydroxyapatite formation and growth in a gelatin gel. Bone Miner 22:147–159 - PubMed
-
- Boskey AL, Spevak L, Paschalis E, Doty SB, Mckee MD (2002) Osteopontin deficiency increases mineral content and mineral crystallinity in mouse bone. Calcif Tissue Int 71:145–154 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

