Patient-reported outcomes in sentinel node-negative adjuvant breast cancer patients receiving sentinel-node biopsy or axillary dissection: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project phase III protocol B-32
- PMID: 20679600
- PMCID: PMC2940391
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.28.2491
Patient-reported outcomes in sentinel node-negative adjuvant breast cancer patients receiving sentinel-node biopsy or axillary dissection: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project phase III protocol B-32
Erratum in
- J Clin Oncol. 2010 Dec 20;28(36):5350
Abstract
Purpose: Sentinel lymph node resection (SNR) may reduce morbidity while providing the same clinical utility as conventional axillary dissection (AD). National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) B-32 is a randomized phase III trial comparing SNR immediately followed by AD (SNAD) to SNR and subsequent AD if SN is positive. We report the definitive patient-reported outcomes (PRO) comparisons.
Patients and methods: Eligible patients had clinically node-negative, operable invasive breast cancer. The PRO substudy included all SN-negative participants enrolled May 2001 to February 2004 at community institutions in the United States (n = 749; 78% age > or = 50; 87% clinical tumor size < or = 2.0 cm; 84% lumpectomy; 87% white). They completed questionnaires presurgery, 1 and 2 to 3 weeks postoperatively, and every 6 months through year 3. Arm symptoms, arm use avoidance, activity limitations, and quality of life (QOL) were compared with intent-to-treat two-sample t-tests and repeated measures analyses.
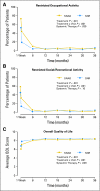
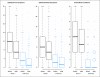
Results: Arm symptoms were significantly more bothersome for SNAD compared with SNR patients at 6 months (mean, 4.8 v 3.0; P < .001) and at 12 months (3.6 v 2.5; P = .006). Longitudinally, SNAD patients were more likely to experience ipsilateral arm and breast symptoms, restricted work and social activity, and impaired QOL (P < or = .002 all items). From 12 to 36 months, fewer than 15% of either SNAD or SNR patients reported moderate or greater severity of any given symptom or activity limitation.
Conclusion: Arm morbidity was greater with SNAD than with SNR. Despite considerable fears about complications from AD for breast cancer, this study demonstrates that initial problems with either surgery resolve over time.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Lyman GH, Giuliano AE, Somerfield MR, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline recommendations for sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7703–7720. - PubMed
-
- Mansel RE, Fallowfield L, Kissin M, et al. Randomized multicenter trial of sentinel node biopsy versus standard axillary treatment in operable breast cancer: The ALMANAC trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:599–609. - PubMed
-
- Fleissig A, Fallowfield LJ, Langridge CI, et al. Post-operative arm morbidity and quality of life. Results of the ALMANAC randomised trial comparing sentinel node biopsy with standard axillary treatment in the management of patients with early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;95:279–293. - PubMed
-
- Zavagno G, De Salvo GL, Scalco G, et al. A randomized clinical trial on sentinel lymph node biopsy versus axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer: Results of the Sentinella/GIVOM trial. Ann Surg. 2008;247:207–213. - PubMed
-
- Gill G. Sentinel-lymph-node-based management or routine axillary clearance? One-year outcomes of sentinel node biopsy versus axillary clearance (SNAC): A randomized controlled surgical trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:266–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

