Allogeneic natural killer cells for refractory lymphoma
- PMID: 20680271
- PMCID: PMC4082975
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-010-0896-z
Allogeneic natural killer cells for refractory lymphoma
Abstract
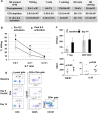
We reported that IL-2 activated autologous NK cells can induce, but not maintain durable remissions in lymphoma patients. We hypothesized that allogeneic NK cells may overcome class I MHC-mediated inhibition of NK cell killing. In a pilot study, we evaluated infusion of haploidentical donor NK cells for antitumor efficacy. Six patients with advanced B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) received rituximab, cyclophosphamide, and fludarabine as immunosupression to permit homeostatic NK cell expansion, followed by CD3-depleted NK cell-enriched cell products followed by subcutaneous IL-2 administration (10 x 10(6) units every other day x 6 doses). At 2 months, four patients showed an objective clinical response. We observed early donor cell persistence in two patients (blood and in tumor-bearing node), but this was not detectable beyond 7 days. All patients demonstrated substantial increases in host-regulatory T cells (Treg) after NK cell and IL-2 therapy (180 +/- 80 cells/microl vs. baseline: 58 +/- 24 cells/microl, p = 0.04) which may have limited donor cell expansion in vivo. These findings suggest safety and feasibility of allogeneic NK cell therapy in patients with lymphoma; however host Treg and inadequate immunodepletion may contribute to a hostile milieu for NK cell survival and expansion. Cell therapy trials should incorporate novel strategies to limit Treg expansion.
Figures
References
-
- Horowitz MM, Gale RP, Sondel PM, Goldman JM, Kersey J, Kolb HJ, Rimm AA, Ringden O, Rozman C, Speck B. Graft-versus-leukemia reactions after bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1990;75:555–562. - PubMed
-
- Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Urbani E, Perruccio K, Shlomchik WD, Tosti A, Posati S, Rogaia D, Frassoni F, Aversa F, Martelli MF, Velardi A. Effectiveness of donor natural killer cell alloreactivity in mismatched hematopoietic transplants. Science. 2002;295:2097–2100. doi: 10.1126/science.1068440. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chalandon Y, Roosnek E, Mermillod B, Waelchli L, Helg C, Chapuis B. Can only partial T-cell depletion of the graft before hematopoietic stem cell transplantation mitigate graft-versus-host disease while preserving a graft-versus-leukemia reaction? A prospective phase II study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006;12:102–110. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2005.09.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Perales MA, Jenq R, Goldberg JD, Wilton AS, Lee SS, Castro-Malaspina HR, Hsu K, Papadopoulos EB, van den Brink MR, Boulad F, Kernan NA, Small TN, Wolden S, Collins NH, Chiu M, Heller G, O’Reilly RJ, Kewalramani T, Young JW, Jakubowski AA (2010) Second-line age-adjusted International Prognostic Index in patients with advanced non-Hodgkin lymphoma after T-cell depleted allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

